Social Media Mental Health Statistics By Negative Effects, Self-Esteem, Impact, And Cyberbullying
Updated · Aug 27, 2024

WHAT WE HAVE ON THIS PAGE
- Introduction
- Editor’s Choice
- Different Social Media Platforms and their uses
- General Social Media Mental Health Statistics
- Social Media And Teens Statistics
- Tips For Managing Social Media Use
- How Common Is Mental Illness?
- Negative Effects Of Social Media On Mental Health
- Social Media Mental Health And Self-Esteem Statistics
- Social Media Mental Health And Parental Concerns
- Impact Of Social Media On Children’s Mental Health
- Cyberbullying And Its Consequences
- Conclusion
Introduction
Social Media Mental Health Statistics: Social media has many uses, but it often causes the most harm to younger users. Teens face significant mental health issues due to social media, and the COVID-19 pandemic made things worse by increasing screen time and social media use. This created more opportunities for teens to encounter online problems, worsening the situation.
Teens also use social media to find communities and interest groups, watch live streams, and support good causes. It’s important to US teens that they feel welcome and safe online. Despite some problems, social media offers many chances for connection and entertainment. We shall shed more light on the Social Media Mental Health Statistics through this article.
Editor’s Choice
- Social Media Mental Health Statistics stated that almost 87% of teens say they have been cyberbullied on social media.
- People who spend over 2 hours a day on social media are 2.7 times more likely to be diagnosed with depression.
- 58% of American adults who use social media feel it harms their mental health.
- Social media use is linked to a 70% increase in self-reported depression symptoms among teens.
- 41% of Gen Z users say social media makes them feel anxious, sad, or depressed.
- Spending too much time on social media raises the risk of developing eating disorders by 2.2 times.
- 50% of people aged 14-24 say Instagram makes them more anxious.
- Using social media is associated with a 9% increase in major depressive episodes over six years.
- Social Media Mental Health Statistics state that almost 71% of people use social media to escape from real-life problems.
- People who use seven or more social media platforms are three times more likely to feel anxious.
- 23% of teens think social media has mostly negative effects on their lives.
- Social media use is linked to a 40% higher risk of sleep problems.
- 60% of social media users say it negatively affects their self-esteem.
- Teens who spend five or more hours a day on screens are 71% more likely to have suicide risk factors.
- 48% of teens who use electronic devices for five or more hours a day have at least one suicide risk factor.
Different Social Media Platforms and their uses
- YouTube (95%) allows users to share videos on various topics, such as music, cooking, makeup tutorials, and vlogs (video blogs).
- TikTok (67%) is a platform for creating short videos from 15 to 60 seconds, mostly for entertainment and comedy but also for informative content. Influencers on TikTok attract followers by sharing quick tips and advice and promoting themselves.
- Instagram (62%) features a 24-hour “stories” option and permanent photo and video posts. Unless an account is set to “private,” anyone can see these posts. Instagram is popular for sharing vacation videos, daily life, and interests in art, cooking, and more.
- Snapchat (59%) lets users share photos that disappear after being viewed and “stories” that vanish after 24 hours. These stories let users share experiences with their followers through photos or videos.
- Facebook (32%) is used for sharing photos, videos, articles, personal information, and chatting with friends.
- These platforms are commonly used to stay in touch with friends and are popular for news and celebrity updates.
| Social Media Platform | % of 13-14 years old using | % of 15-17 years old using |
| 23 |
39 |
|
|
Snapchat |
51 | 65 |
| 45 |
73 |
|
|
TikTok |
61 | 71 |
| YouTube | 94 |
95 |
General Social Media Mental Health Statistics
- Nearly 71% of social media users think it’s important to take breaks from it.
- 45% of people on social media feel overwhelmed by the amount of information they see.
- Roughly 24% of teenagers believe social media mostly has a negative impact on their lives.
- 70% of teenagers check social media several times a day.
- Around 59% of adults say social media affects their mental health.
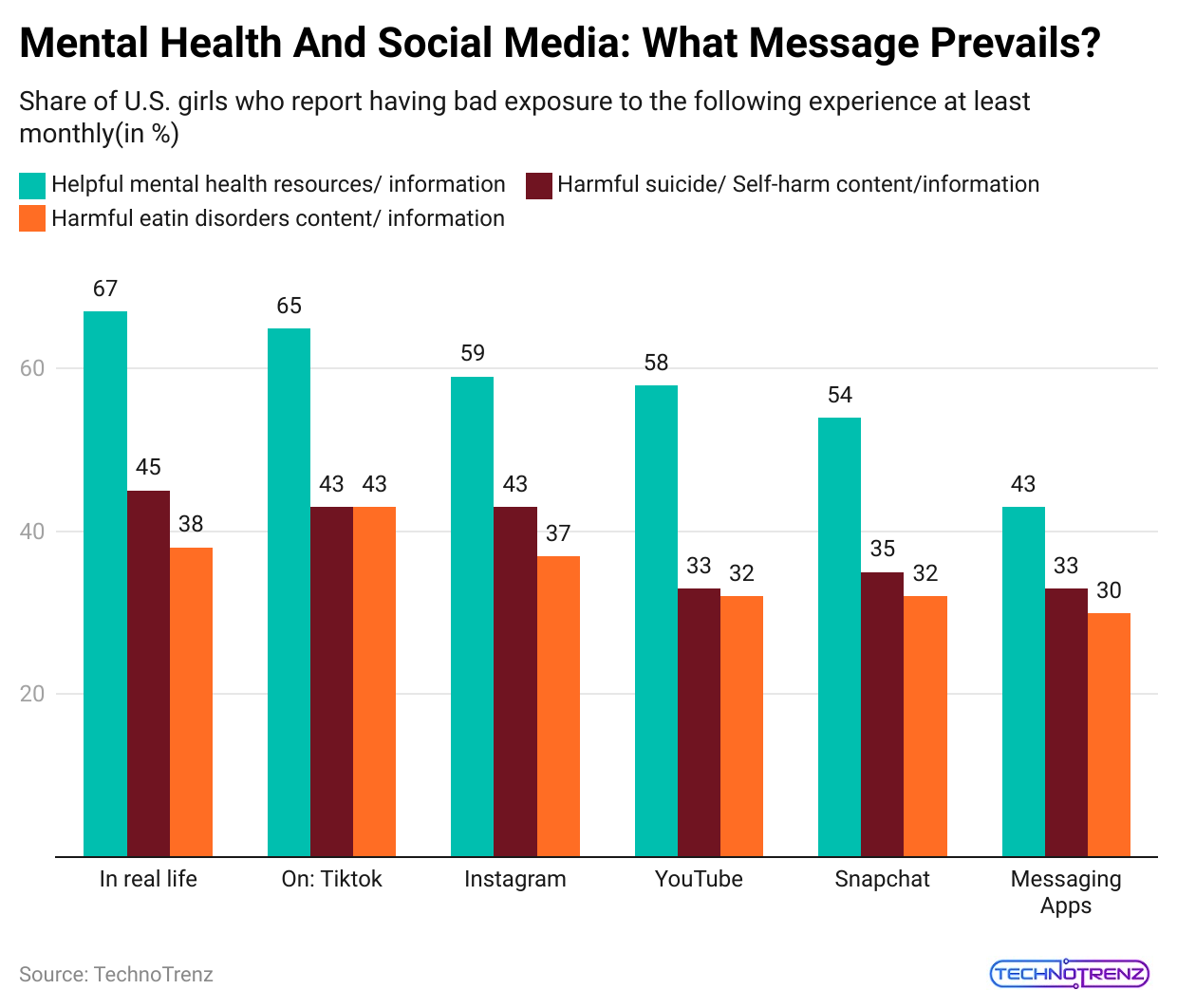 (Reference: statista.com)
(Reference: statista.com)
- Nearly 41% of women on social media feel pressured to present themselves a certain way.
- 63% of people on social media feel lonely.
- 37% of social media users experience FOMO (fear of missing out).
- Social Media Mental Health Statistics stated that almost 63% of parents think social media harms their children’s mental health.
- Almost 32% of teenagers report being cyberbullied.
- 40% of social media users feel anxious or depressed after using it.
- Around 60% of people on social media feel they need to take a break from it.
- 70% of teenagers think social media platforms don’t do enough to stop cyberbullying.
- Approximately 42% of social media users feel more insecure about their appearance after using it.
- Near 37% of social media users are negatively affected by political discussions online.
Social Media And Teens Statistics
- 41% of teens who use social media the most rate their mental health as poor or very poor, as per Social Media Mental Health Statistics.
- This is higher than the 23% of teens who use social media the least. For instance, 10% of heavy social media users have had thoughts of suicide or self-harm in the past year, compared to 5% of light users.
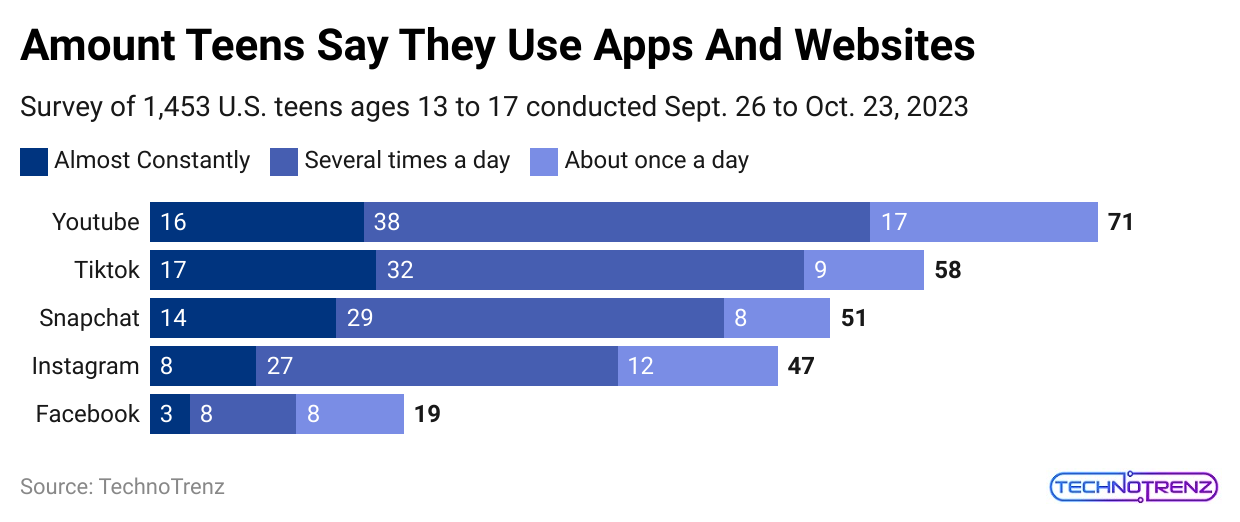 (Reference: axios.com)
(Reference: axios.com)
- Additionally, 17% of heavy users feel poor about their body image, while only 6% of light users feel the same.
- On average, US teens spend 4.8 hours each day on seven popular social media apps.
- YouTube, TikTok, and Instagram make up 87% of their social media time.
- Specifically, 37% of teens use these apps for five or more hours a day, 14% use them for 4 to less than 5 hours, 26% use them for 2 to less than 4 hours, and 23% use them for less than 2 hours a day.
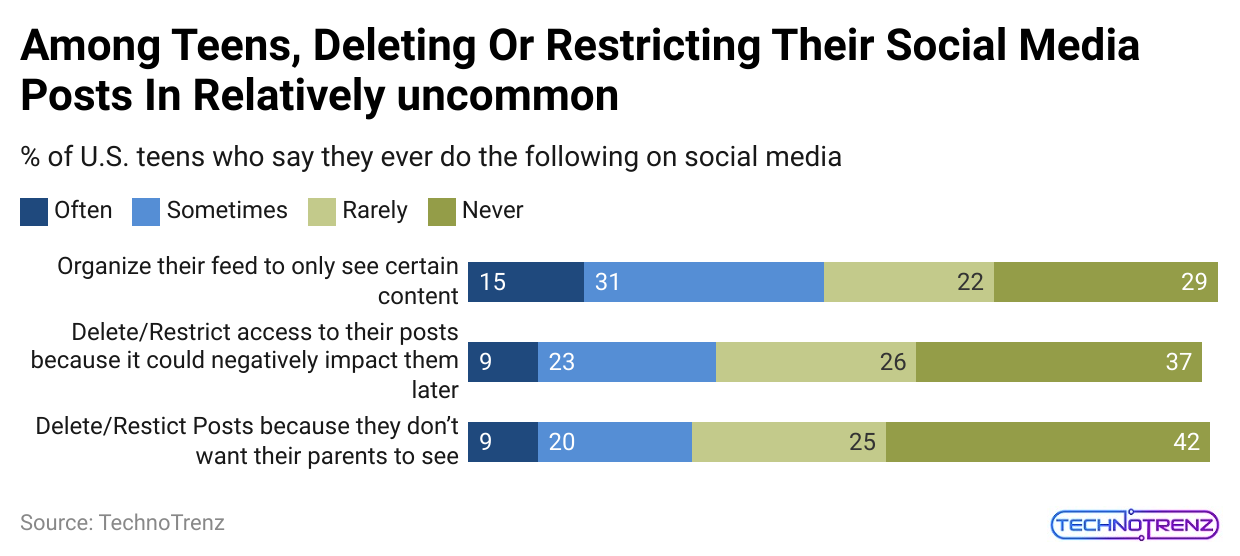
(Reference: pewresearch.org)
| Often | Sometimes | Rarely | Never | |
| Organize their feed only to see certain content | 15 | 31 | 22 |
29 |
|
Delete/Restrict access to their posts because it could negatively impact them later |
9 | 23 | 26 | 37 |
| Delete/Restrict posts because they don’t want their parents to see | 9 | 20 | 25 |
42 |
- 60% of high-frequency social media users with low parental supervision and weak family relationships report poor mental health.
- This compares to 25% of high-frequency users who have strong parental supervision and good family relationships.
- Moreover, 22% of high users with low-income family relationships and monitoring have thoughts of suicide or self-harm, compared to 2% of high users with strong family support.
- Strong family relationships and monitoring help reduce mental health issues, even among teens with high social media use.
Tips For Managing Social Media Use
- Set a time each night after which you won’t check your phone. Charge your phone in another room while you sleep.
- Use an alarm clock instead of your phone to wake up, and you won’t have to use your phone first thing in the morning.
- Pick one day a week to take a break from social media and focus on other activities.
- Turn off your notifications for a few hours each day, and consider using “Airplane” mode or “Do Not Disturb” to minimize distractions.
- Set specific times for checking your notifications instead of constantly checking throughout the day.
- Take breaks from apps that negatively affect your body image or self-esteem. Try using apps designed to improve your well-being, like meditation apps.
- Use apps that track your usage and block other apps to help you become more aware of your screen time and encourage you to engage in other activities.
- Develop a habit of placing your phone near the door when you get home. Doing this with friends or family can help you stay committed. Plan regular in-person hangouts with friends instead of just interacting online.
- Consider changing your phone’s display to grayscale. This makes your phone less appealing and might help you ignore it more easily.
- Seek help if you experience online harassment or abuse. Talk to trusted people like family members, friends, teachers, or counselors, and check resources on how to report cyberbullying.
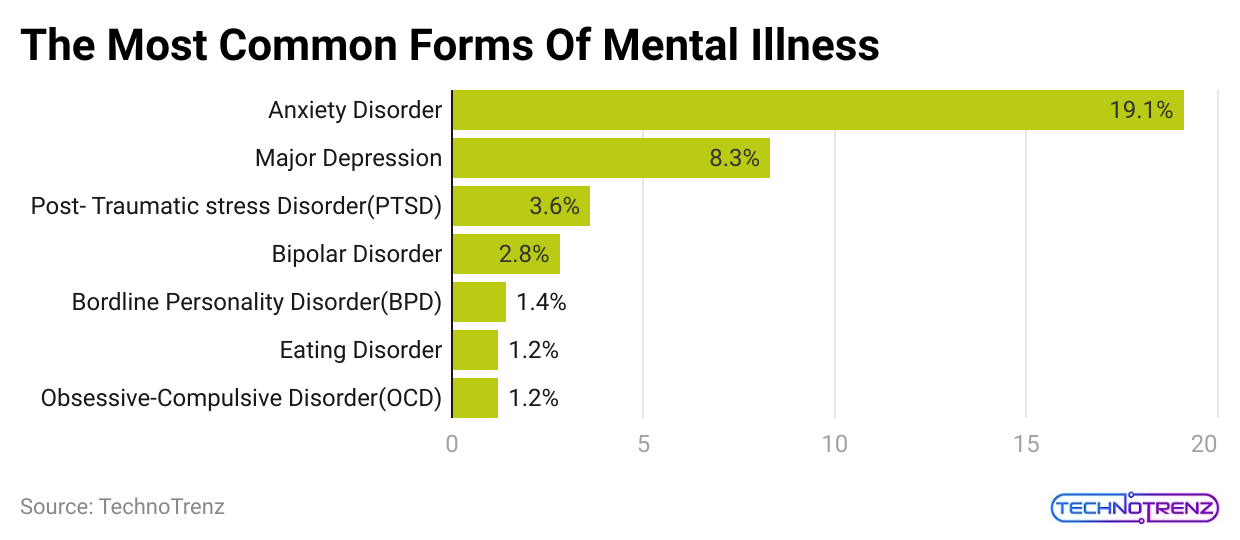
How Common Is Mental Illness?
- 13% of people worldwide have mental health issues.
- In the US, 1 in 5 adults deal with mental illness each year, and 1 in 20 face serious mental health problems annually.
 (Reference: usa.edu)
(Reference: usa.edu)
- 1 in 6 children in the US, aged 6 to 17, experience a mental health disorder each year.
- The COVID-19 pandemic has impacted the mental health of 59% of people in the US.
- Globally, 970 million people have mental health or substance abuse disorders.
- Social Media Mental Health Statistics state that almost 284 million people around the world suffer from anxiety.
- Mental illness affects more women (11.9%) than men (9.3%).
- People with mental health disorders generally have a lower life expectancy, losing an average of 10.1 years.
- Mental disorders account for about 14.3% of global deaths, which is roughly 8 million deaths each year.
Negative Effects Of Social Media On Mental Health
- 48% of young adults say social media harms their relationships.
- Almost 37% of teens feel pressured to post content that will be popular and get likes.
- 56% of social media users feel anxious when comparing themselves to their friends.
- Nearly 42% of social media users have felt envious of other people’s life experiences.
- 64% of people say social media increases their feelings of loneliness, as stated by Social Media Mental Health Statistics.
- Around 36% of UK adults believe social media worsens their stress levels.
- 61% of adults feel lonelier because of the pandemic, and social media use makes it worse.
 (Reference: statista.com)
(Reference: statista.com)
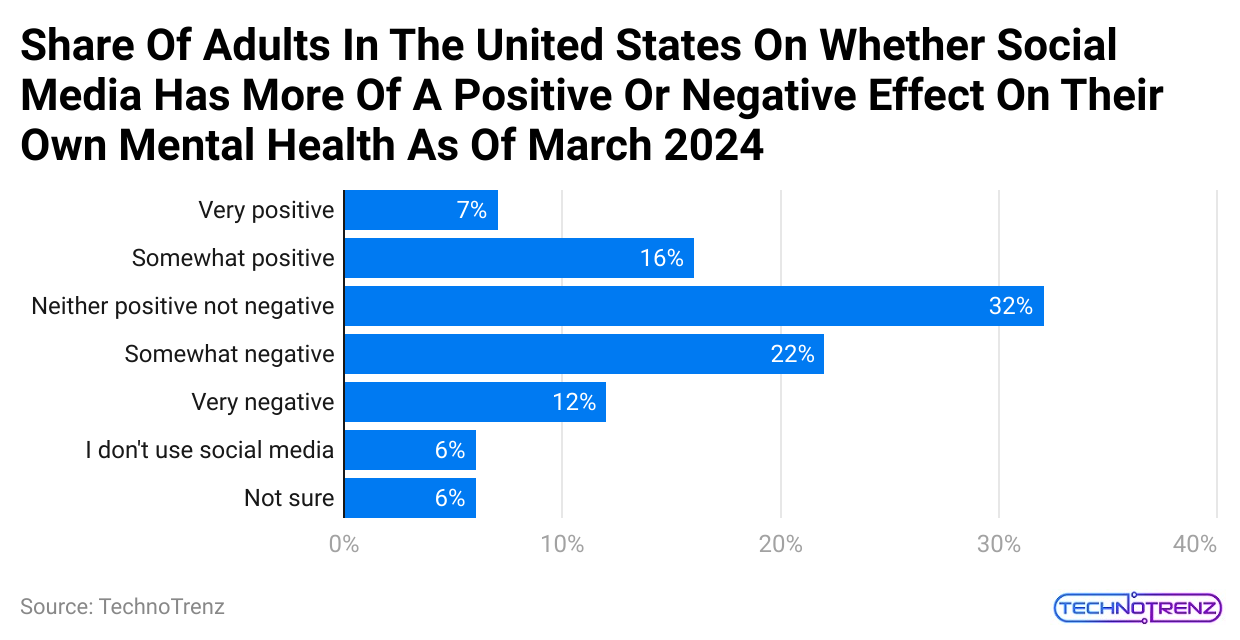
In a survey conducted in March 2024 in the United States:
- 32% of adults said social media didn’t affect their mental health, either positively or negatively.
- 7% felt that social media had a very positive impact on their mental health.
- 12% thought social media had a very negative effect on their mental health.
- 22% of people said social media hurt their mental health.
Almost 62% of adults think social media hurts society.
- 37% of social media users feel pressured to create a perfect online image.
- Social Media Mental Health Statistics stated that almost 60% of people using social media say it negatively affects their self-esteem.
- 65% of adults feel overwhelmed by the amount of information on social media.
- 55% of social media users think others portray an overly positive image of their lives.
- Social Media Mental Health Statistics stated that almost 38% of adults using social media feel lonely when compared to others.
- 52% of teens using social media have deleted posts to avoid negative feedback.
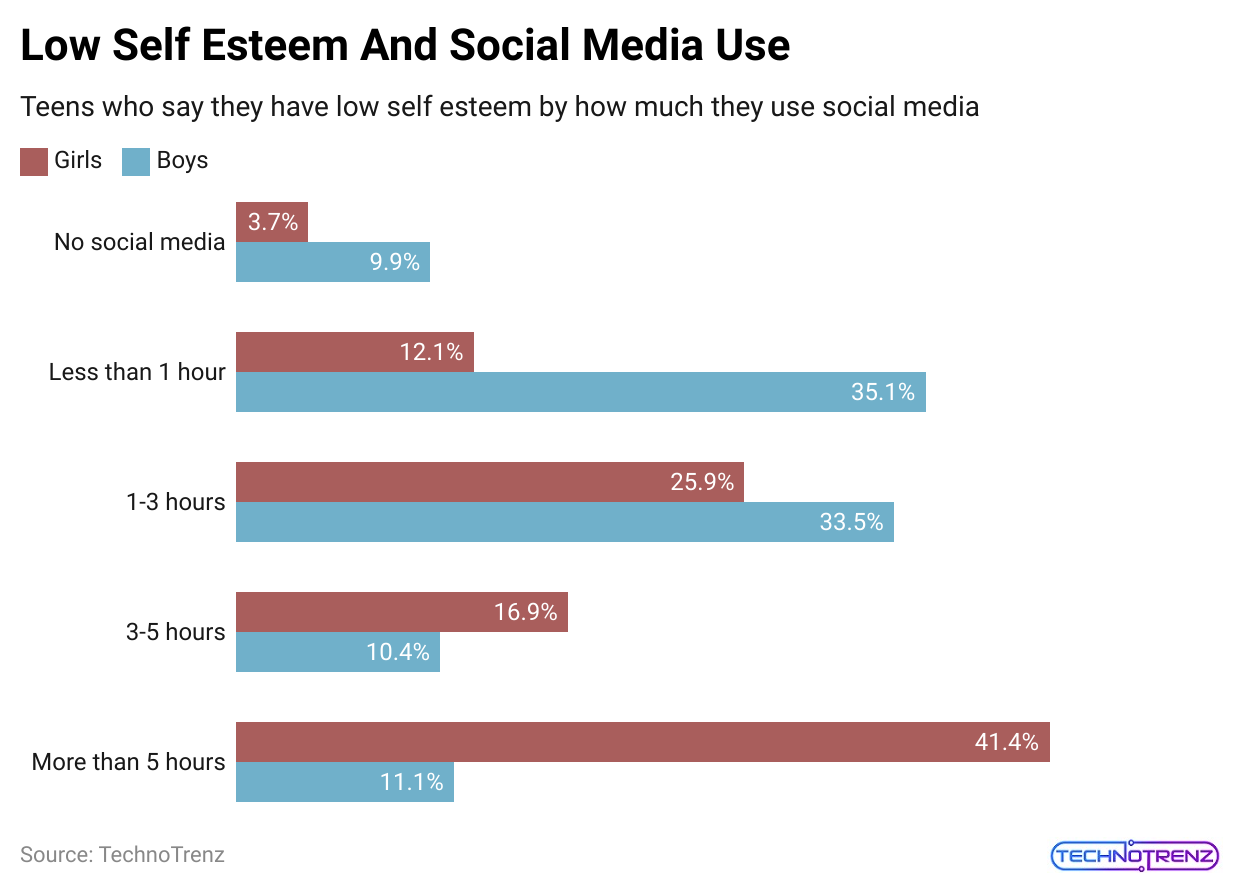
Social Media Mental Health And Self-Esteem Statistics
- 60% of people say social media hurts their self-esteem.
- 42% of people feel jealous or left out when using social media.
- 56% of social media users feel excluded when they see photos of friends at events they weren’t invited to.
 (Reference: medium.com)
(Reference: medium.com)
- 62% of people feel their own life and achievements are lacking when they compare themselves to others on social media.
- Using social media is linked to a 60% higher risk of developing low self-esteem.
- 39% of social media users feel envious of others’ seemingly perfect lives.
- Social Media Mental Health Statistics stated that roughly 52% of social media users feel worse about their own life after viewing friends’ posts.
- 43% of teenagers feel pressured to post content that will get likes and comments.
- Social media use is associated with a 40% higher risk of developing narcissistic traits.
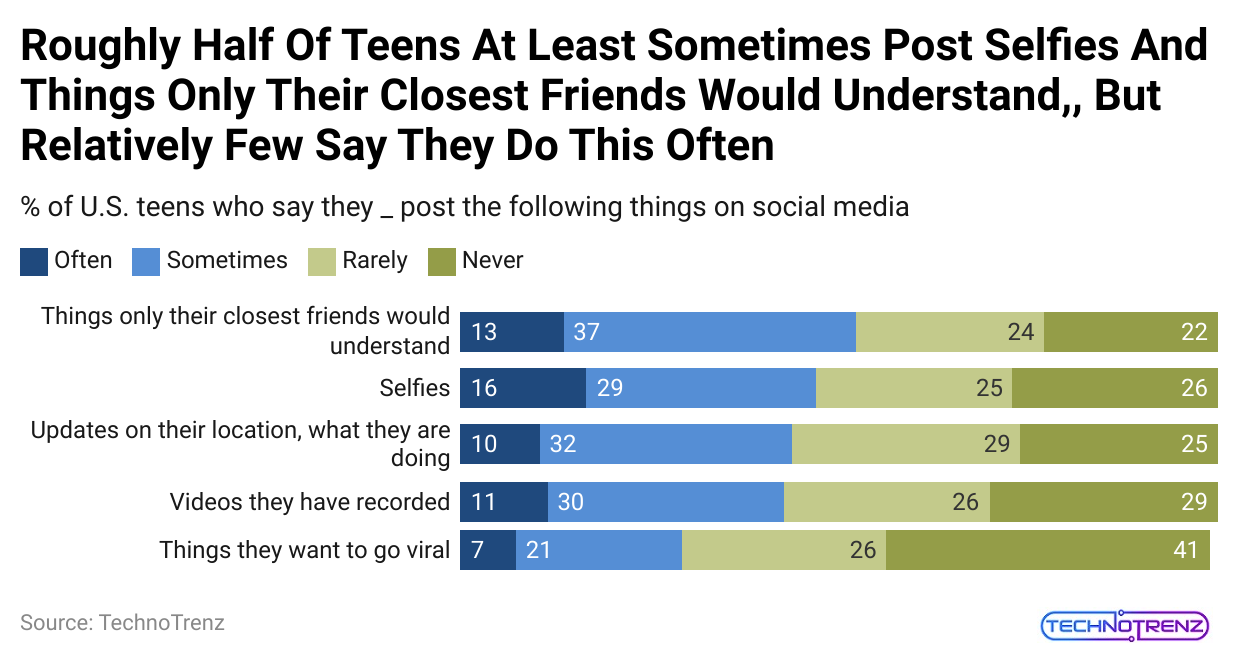
(Reference: pewresearch.org)
| Often | Sometime | Rarely | Never | |
| Things only their closest friends would understand | 13 | 37 | 24 |
22 |
|
Selfies |
16 | 29 | 25 | 26 |
| Updates on their location, what they’re doing | 10 | 32 | 29 |
25 |
|
Videos they’ve recorded |
11 | 30 | 26 | 29 |
| Things they want to go viral | 7 | 21 | 26 |
41 |
- Social media use is connected to a 30% higher risk of developing perfectionism.
- Social media use is linked to a 25% higher risk of developing imposter syndrome.
- 53% of social media users feel upset when their posts don’t get as many likes or comments as they hoped.
Social Media Mental Health And Parental Concerns
- A 2023 survey showed that most US parents think social media is partly responsible for the rise in teenage depression.
- Instagram is the platform they are most worried about, followed by Snapchat and TikTok.
- As of June 2020, 58% of parents said social media use causes their teens not to get enough sleep.
- Parents are also concerned that social media makes their teens seek too much approval or attention and experience bullying.
- Additionally, 17% of parents believe social media makes their teens feel angry, and 15% think it makes them feel depressed.
Impact Of Social Media On Children’s Mental Health
- Almost 71% of Gen Z and 61% of Millennials say social media impacts their well-being.
- Nearly 40% of social media users report negative effects on their mental health.
- 39% of social media users feel worse about their own lives after seeing other people’s posts.
- Around 29% of social media users have felt depressed because of social media.
- Social Media Mental Health Statistics stated that almost 57% of social media users have taken a break from these platforms to protect their mental health.
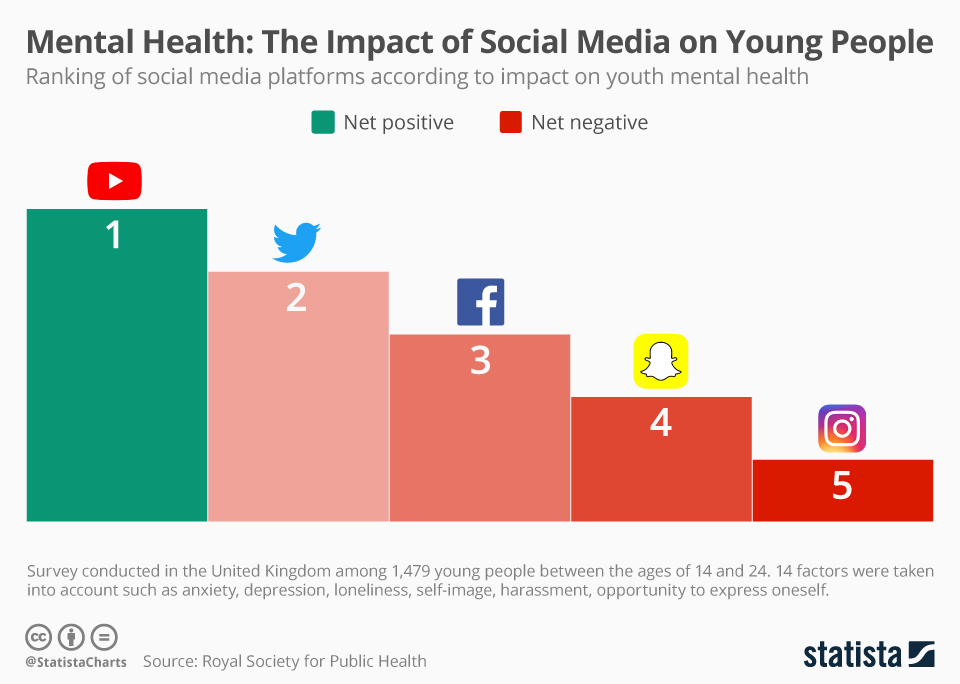
(Source: statista.com)
- 75% of teenagers in the US have set up social media accounts.
- Almost 58% of US teens say social media makes them feel anxious.
- 47% of American adults feel lonely, as per Social Media Mental Health Statistics.
- 46% of teens have seen false or misleading information about mental health on social media.
- As per Social Media Mental Health Statistics, almost 28% of teenagers have experienced depression related to social media.
- 41% of social media users have removed tags from photos to avoid negative judgment.
- 53% of teenagers worry about their appearance in photos posted online.
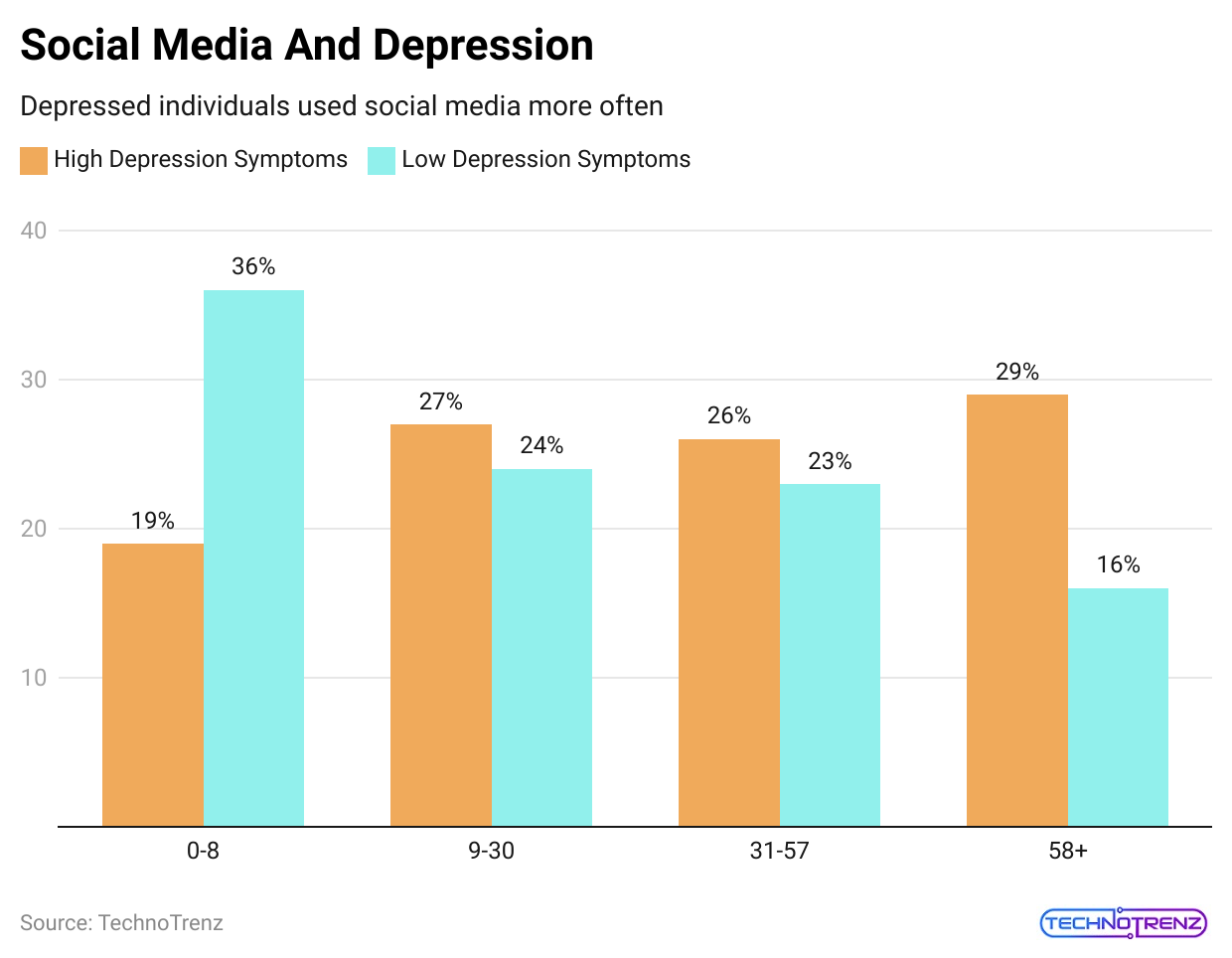
(Reference: clearvuehealth.com)
- In the above chart, we can see the Social Media and Depression Statistics in various age groups.
|
Age Group |
High Depression Symptoms | Low Depression Symptoms |
| 0-8 | 19% |
36% |
|
9-30 |
27% | 24% |
| 31-57 | 26% |
23% |
|
58+ |
29% |
16% |
- Nearly 29% of social media users say online conflicts have affected their mental health.
- 76% of female social media users worry about body image from comparing themselves to others online.
- 41% of social media users report having sleep problems linked to social media use.
Cyberbullying And Its Consequences
- Cyberbullying is when people use online platforms, like social media, to bully or threaten others.
- It’s a widespread problem among kids and teenagers. Studies show that almost 34% of children have been cyberbullied at some time, and 10% have been targeted in the past 30 days.
- The effects of cyberbullying go beyond just causing emotional pain, as per Social Media Mental Health Statistics.
- Teenagers who are cyberbullied are more likely to develop mental health problems like depression, anxiety, low self-esteem, and suicidal thoughts.
- Additionally, it can lead to school difficulties, drug use, and feelings of loneliness.
| Consequences | Description |
| Loneliness |
Victims often feel isolated from their peers, leading to feelings of loneliness. |
|
Substance Use |
There’s a significant association between cyberbullying and substance use. |
| Academic Problems |
Victims may experience difficulties in concentrating, leading to poor academic performance. |
|
Mental Health Issues |
Increased risk of depression, anxiety, low self-esteem, and suicidal thoughts. |
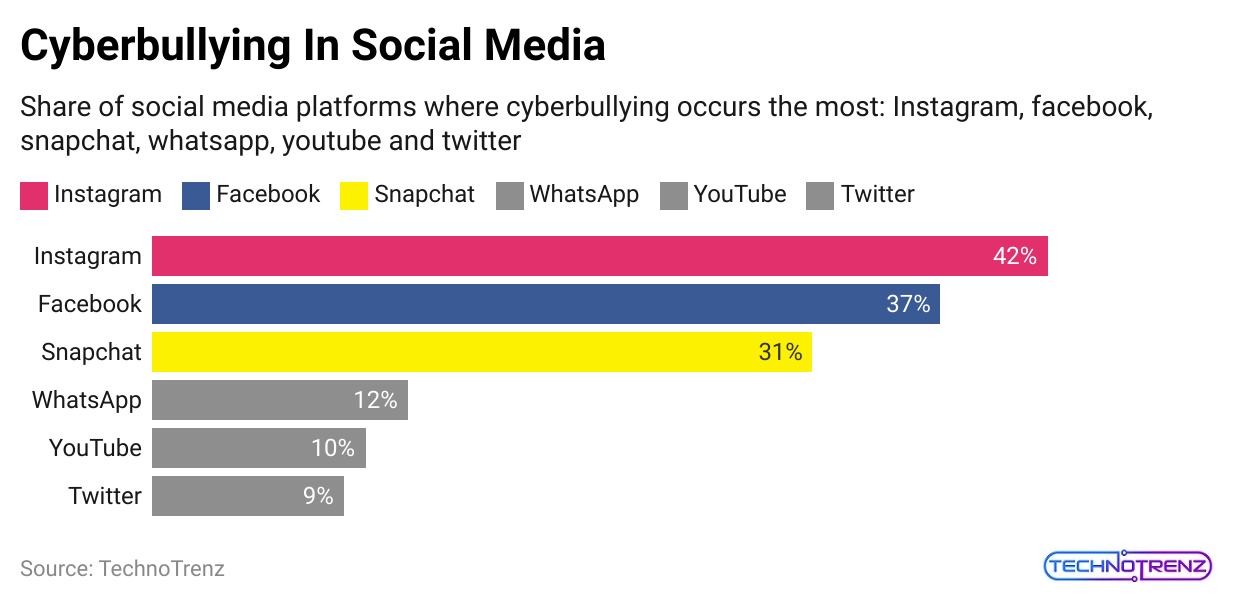
(Reference: firstsiteguide.com)
- There are clear differences between genders when it comes to cyberbullying. Girls are more likely to be affected than boys.
- Approximately 36.4% of girls have faced cyberbullying, compared to 31.4% of boys. These differences might be because boys and girls use and experience social media in different ways.
Conclusion
Well, everyone, we’ve had quite a look at social media, and the numbers are clear. Whether you’re into TikTok, a big fan of Facebook, or scroll casually, it’s obvious that social media has a strong grip on us. From the excitement of staying connected to the risks of too much use, social media addiction is a real issue with both ups and downs. As we navigate this fast-changing digital world, it’s important to find a balance between our online and offline lives. So, take breaks, breathe deeply, and maybe even put down your phone for a bit. We have shed enough light on the Social Media Mental Health Statistics through this article.
Sources
FAQ.
Social media has a big impact on mental health. It can help people feel more connected, boost self-esteem, and make them feel like they belong. But it can also create stress, pressure people to compare themselves to others and lead to feelings of sadness and loneliness. It’s important to use social media carefully to avoid these problems.
Research indicates that people who use social media excessively often perform worse on mental tasks than those who use it less. This may be because social media demands a lot of attention, making it harder for heavy users to focus and avoid distractions.

Joseph D'Souza started Techno Trenz as a personal project to share statistics, expert analysis, product reviews, and tech gadget experiences. It grew into a full-scale tech blog focused on Technology and it's trends. Since its founding in 2020, Techno Trenz has become a top source for tech news. The blog provides detailed, well-researched statistics, facts, charts, and graphs, all verified by experts. The goal is to explain technological innovations and scientific discoveries in a clear and understandable way.