Introduction
AI Job Loss Statistics: In recent years, AI has been reshaping many workplaces, intensifying concerns about job losses across sectors. Because of this, many people are worried about one thing: how many jobs could disappear, and when they might happen. News stories often present a single large number, but the truth is not that simple. Different reports yield different results because they examine different details. Some studies count only the parts of a job that a computer can perform, rather than the full job.
Jobs may gradually become smaller as more companies adopt AI. A few reports primarily discuss rapid job cuts in work that is easy to repeat and simple to follow. In this article, on AI Job Loss Statistics, we will cover factors that are getting affected by AI, including industry, income level, region, and access to retraining, that must be considered. All current reports and analyses draw on distinct insights to explain what the figure depicts, the time span it covers, and whether it shows only job cuts or the net change after new jobs are created.
Editor’s Choice
- A report published by Trueup indicates that in 2025, there were 711 layoff events, affecting 209,429 people, with about 597 per day.
- According to a report by Exploding Topics, AI could eliminate more than 300 million jobs in 2025.
- On July 24, 2025, Intel announced layoffs affecting 21,400 employees across the company.
- 74.08 million women’s jobs are affected (79%), and 84.21 million men’s jobs are affected (58%).
- According to Demand Sage reports, around 92 million jobs will be replaced by 2025.
- AI may automate 80% of customer service representative tasks.
- As of 2025, total U.S. job losses attributable to AI and automation amount to 1.8% of the workforce.
- In 2025, the most exposed sectors will be those with high levels of automatable tasks, with chatbots accounting for administration (26%) and customer service (20%).
- In the same period, automation accounted for 2.6% of employment shifts in developed economies, compared with 0.9% in developing economies.
- Bloomberg Intelligence reports that AI may replace tasks and that banks could cut 200,000 jobs over 3 to 5 years.
- By 2030, job losses are expected to reach approximately 256 million in China.
General AI Job Loss Statistics
- A report published by Exploding Topics states that in 2025, AI can eliminate more than 300 million jobs.
- By 2030, AI may push 14% of workers (375 million) to switch careers.
- In the United States, around 47% of employees could have parts of their roles threatened by AI within the next decade.
- Turning about half of today’s tasks into automated work might still take 20 years worldwide.
- In high-income economies, 60% of jobs are highly exposed, whereas in low-income nations only 26% are.
- 3% of people without a high school diploma hold jobs labelled “most exposed.”
- Moreover, people aged 18-24 are 129% more likely than those aged 65+ to fear that their job will disappear.
- Only 15% would accept an AI boss.
- The PatentPC report further estimated that by 2030, nearly 20 million manufacturing jobs will be displaced by automation.
- By the end of 2027, approximately 7.5 million data-entry jobs will be lost.
- As of 2025, AI is expected to displace approximately 36 million workers, according to techjury.net.
- Around 36 million Americans have jobs threatened by automation.
- More than 40% of workers with low levels of education will be displaced by 2030, compared with 10% of workers with high levels of education.
- By 2040, automation may result in approximately 12 million job losses across Europe.
- In the United Kingdom, AI is expected to displace approximately 7 million jobs between 2017 and 2037.
Impact Of AI On The Current Job Market Statistics

(Source: buttercms.com)
- In the United States, 30% of companies reported that AI tools, such as ChatGPT, had replaced employees in 2024, while this could rise to 38% by 2025.
- From January to early June 2025, AI was directly blamed for 77,999 tech layoffs.
- Among firms adopting AI, 40% use it to automate tasks rather than support staff.
- Since 2000, automation has erased 1.7 million manufacturing roles.
- In the U.S., 13.7% stated that a robot cost them their job today.
Tech Employees Layoffs Statistics
- According to finalroundai.com, the total tech layoffs due to AI in January 2025 accounted for 16,033 employees, followed by February (19,029), March (11,003), April (6,337), May (24,467) and June (1,130).
- A report published by Trueup indicates that in 2025, there were 711 layoff events, affecting 209,429 people, with about 597 per day.
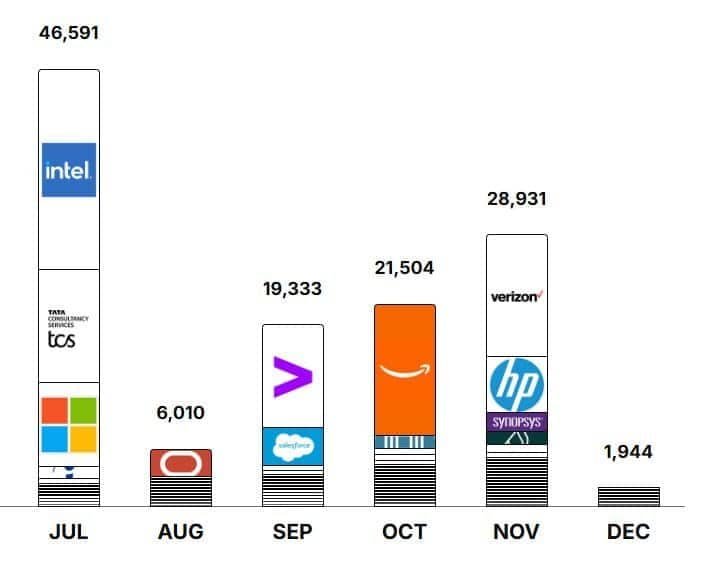
- In 2025, the total number of employee layoffs linked to AI was 46,591 in July, then fell to 6,010 in August.
- They rose again to 19,333 in September, increased to 21,504 in October, and reached 28,931 in November.
Company-Wise Employee Layoffs
(Source: trueup.io)
- On July 24, 2025, Intel announced layoffs affecting 21,400 employees across the company.
- Meanwhile, on August 22, Oracle cut 2,882 jobs; on September 27, Accenture reduced 11,000 roles; on October 28, Amazon eliminated 14,000 positions; and on November 20, Verizon laid off 13,000 employees.
Others are stated in the table below:
| July | September | October | November |
| July 25, TCS (12,000) |
September 2 Salesforce (4,000) |
October 23 Applied Materials (1,400) |
November 25 HP (6,000) |
| July 2 Microsoft (9,000) |
– | – | November 12 Synopsys (2,000) |
| – | – | – | November 10 Sonder (1,421) |
- In 2025, large scale layoffs highlighted how automation, AI adoption, and cost restructuring reshaped global workforce strategies across technology and enterprise sectors.
- Intel reported the single largest workforce reduction, cutting 21,400 jobs in July 2025, reflecting efficiency drives in semiconductor manufacturing and AI focused restructuring.
- Amazon conducted multiple layoffs in 2025, removing a combined 14,000+ roles earlier in the year and an additional 84 positions in December, linked to automation and operational streamlining.
- Accenture reduced 11,000 jobs in September 2025, as enterprise clients shifted spending toward AI led consulting and digital automation tools.
- Microsoft eliminated 9,000 roles in July 2025, aligning teams around AI first productivity platforms and cloud optimization.
- TCS announced major layoffs twice in 2025, cutting 12,000 jobs in July and another 365 roles in December, signaling cost control amid AI driven delivery models.
Furthermore, other companies’ layoffs from November 28 to December 15, 2025, are mentioned below:
| Date | Company Name | Number of Layoffs |
|
28-Nov |
Thunderful | 60 |
| – | Covalen | 400 |
| 1-Dec | TCS | 365 |
| 2-Dec | Outright Games | 27 |
| – | Panasonic | 70 |
| – | Eidos-Montreal | 12 |
| 3-Dec | Cellebrite | 20 |
| 4-Dec | GXS Bank | 82 |
| 5-Dec | Wunderkind | 50 |
| 8-Dec | Payoneer | 144 |
| – | Mobileye | 200 |
| 9-Dec | Glowmade | 12 |
| – | VSCO | 24 |
| – | Tenstorrent | 75 |
|
10-Dec |
SE Ranking | 36 |
| – | Teads | 180 |
| – | Lusha | 24 |
| 12-Dec | Rakuten | 100 |
| – | TikTok | 30 |
| – | Amazon | 84 |
- Verizon laid off 13,000 employees in November 2025, driven by network automation and AI-based customer service systems.
- Oracle reduced its workforce by 2,882 roles in August 2025, as enterprise software operations adopted AI-enabled efficiency programs.
- HP announced 6,000 job cuts in November 2025, reflecting automation in hardware operations and AI-assisted supply chain management.
- Salesforce eliminated 4,000 positions in September 2025, following deeper integration of AI across sales, marketing, and support workflows.
- Synopsys reduced its workforce by 2,000 in November 2025, as AI-optimised chip design tools reduced manual engineering requirements.
- Applied Materials cut 1,400 roles in October 2025, linked to productivity gains from AI-enhanced manufacturing processes.
- Mobileye laid off 200 employees in December 2025, as AI automation improved efficiency in autonomous driving development.
- Payoneer reduced 144 positions in December 2025, reflecting AI-driven changes in fintech operations and compliance workflows.
- Across smaller firms between late November and mid December 2025, over 1,500+ additional jobs were eliminated, showing that AI-related workforce impact extended beyond large enterprises into mid-sized and emerging companies.
AI Job Replacement Estimates Statistics
- According to Demand Sage reports, around 92 million jobs will be replaced by 2025.
- With a 2024 global labour force of 3.7 billion, AI could replace 8.1% of workers.
- The IMF says AI may affect nearly 40% of jobs worldwide. Across 21 OECD countries, OECD analysis finds 27% of jobs are at high risk of AI.
- As of 2025, 40% of employers report aiming to reduce staff by 40%.
- In the first half of 2025, 77,999 tech job losses were directly attributed to AI.
- In the US, 49% of companies using ChatGPT report replacing workers.
- By 2030, up to 20 million manufacturing jobs could be displaced globally.
- Meanwhile,14% of workers may need to transition to new careers, and 30% of U.S. jobs could be displaced.
- By 2050, 60% possibly 80% of jobs may be automated or transformed, influencing 26% of global GDP, about USD 15.7 trillion, especially in healthcare, transportation, finance, and retail.
AI Job Replacement Statistics by Work Type
- Over the next 1 to 5 years, AI could lower hiring for white-collar entry-level roles by about 10% to 20%.
(Reference: demandsage.com)
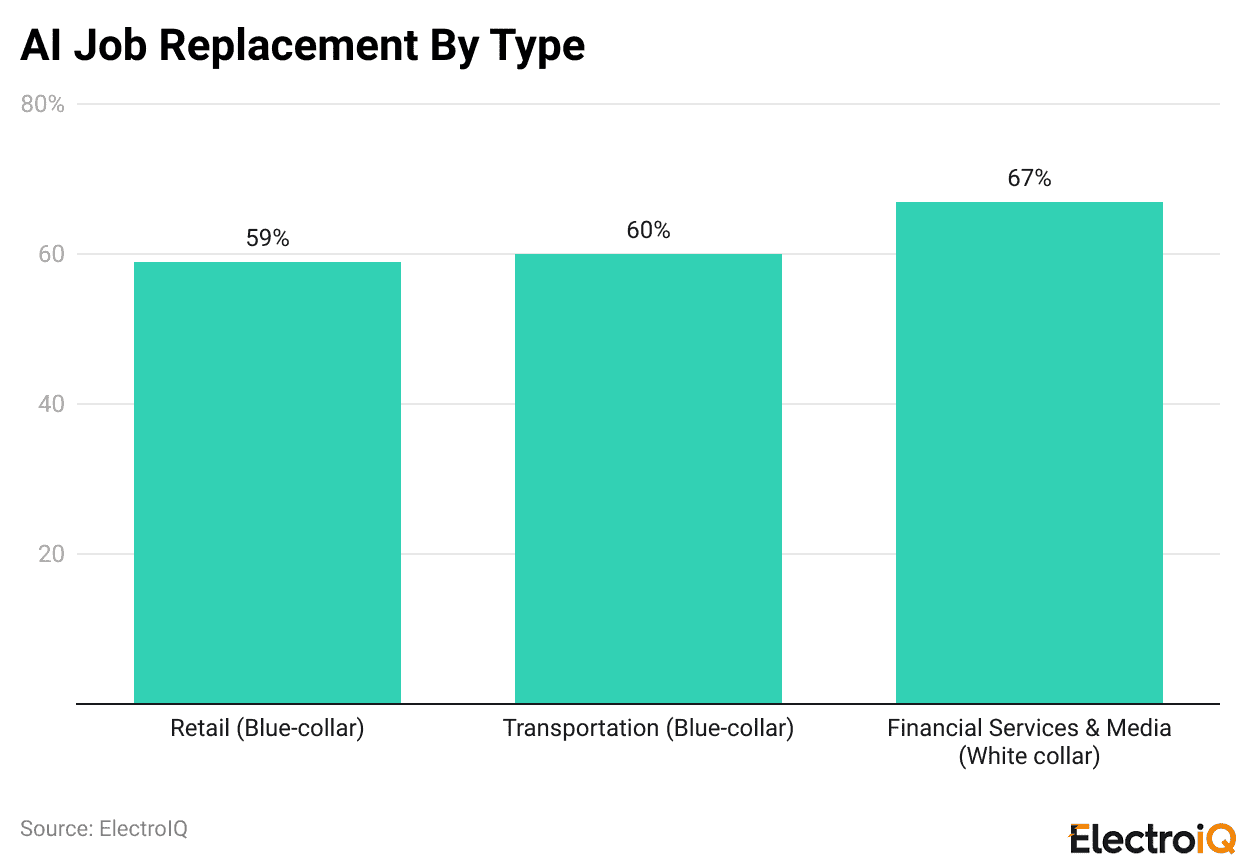
- Automation concerns are greatest among white-collar jobs (67%), transport (60%), and retail (59%).
- By 2025, around 40% of university graduates may choose trade jobs instead.
- Many professionals (52%) agree that trade work is less likely to be replaced.
- Another trend indicates that AI slightly reduces the share of low-skill employment by 0.001% per AI unit.
- Across 21 OECD countries, about 9% of jobs are considered at risk.
Gender Exposure To AI Job Loss Statistics
(Source: aiprm.com)
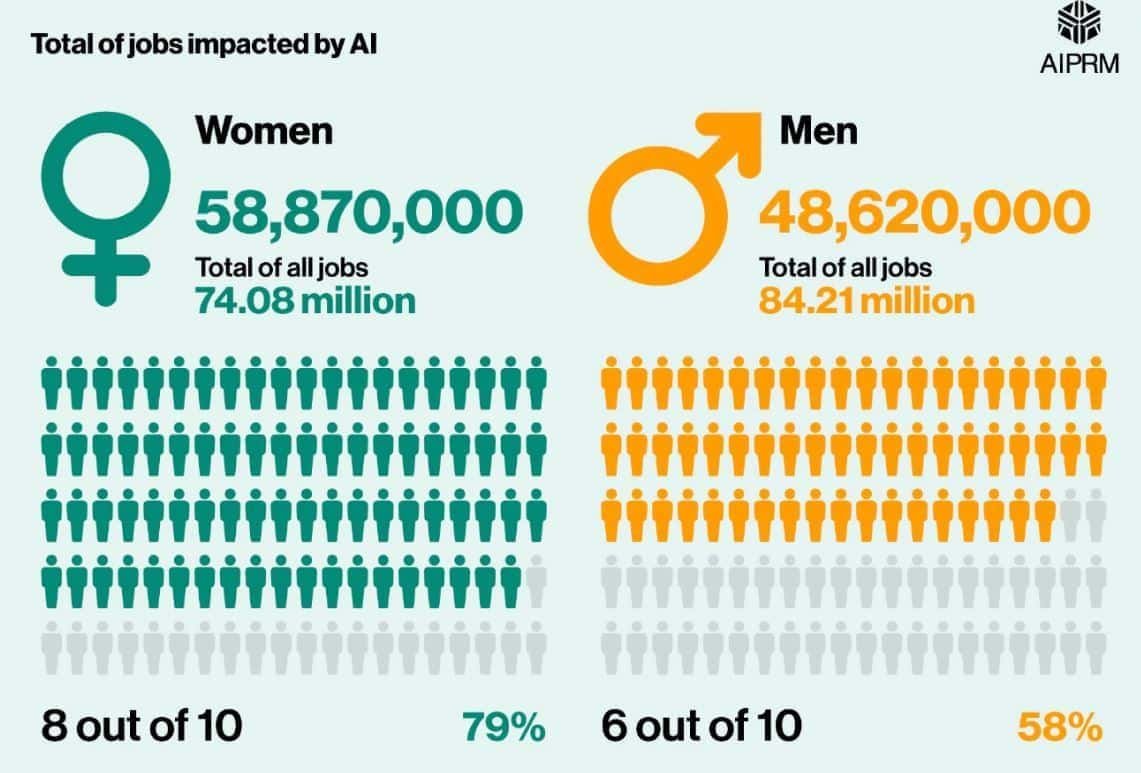
- In the United States, 8 out of 10 women, with about 58.87 million (58,870,000), are in jobs highly exposed to generative AI automation.
- Among men, the proportion is 6 out of 10, corresponding to approximately 48.62 million.
- Overall, 21% more women than men are exposed to AI automation risk.
- The above chart shows that 74.08 million women’s jobs (79%) are affected, and 84.21 million men’s jobs (58%) are affected.
- It also notes that women constitute approximately 70% of white-collar workers and 30% of blue -collar workers.
- Men are more evenly distributed, at roughly 50/50.
United States Jobs Lost To AI And Automation Statistics
(Source: licdn.com)
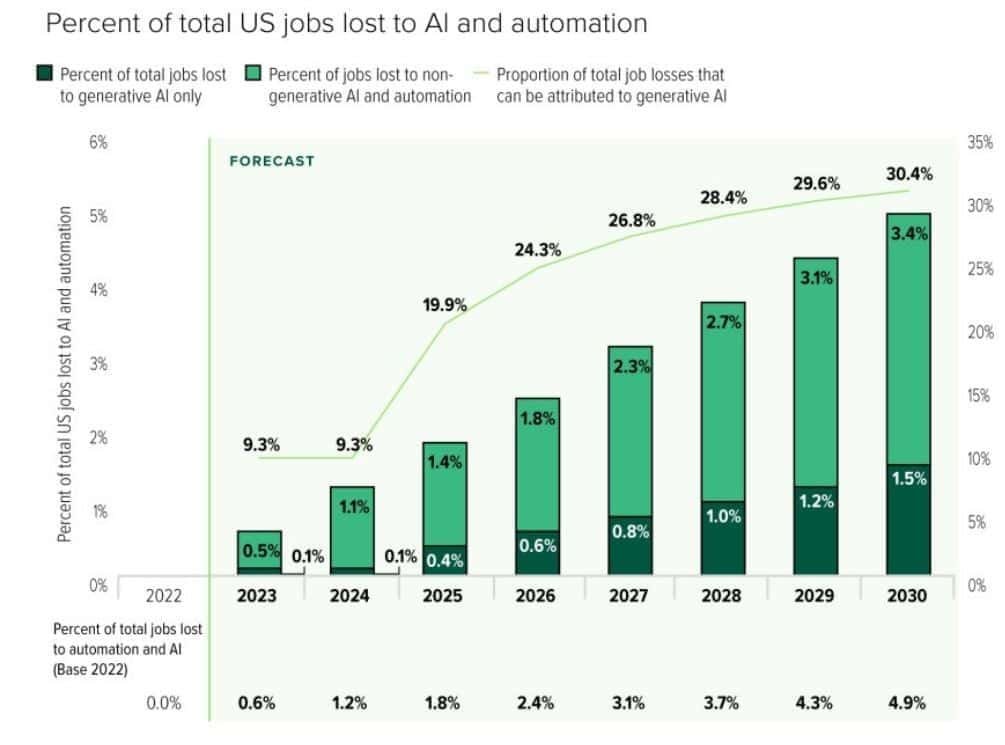
- As of 2025, AI and automation together account for 1.8% of total U.S. workforce displacement, indicating a measurable but still controlled impact on employment.
- Non-generative automation remains the primary driver, responsible for 1.4% of job losses, reflecting long-term adoption of rule-based systems and robotics.
- Generative AI accounts for 0.4% of total job displacement, showing an early yet fast-rising influence across white-collar roles.
- Despite its smaller base, generative AI already accounts for 19.9% of all AI-related job losses, underscoring its greater disruption intensity.
In the coming years, the estimated analyses are stated below:
| Year | Total U.S. jobs lost to AI & automation | Non-generative AI & automation | Generative AI only | Gen-AI share of losses |
| 2026 | 2.4% | 1.8% | 0.6% | 24.3% |
| 2027 | 3.1% | 2.3% | 0.8% | 26.8% |
| 2028 | 3.7% | 2.7% | 1% | 28.4% |
| 2029 | 4.3% | 3.1% | 1.2% | 29.6% |
| 2030 | 4.9% | 3.4% | 1.5% | 30.4% |
- Generative AI’s share of workforce impact is projected to increase to 24.3% in 2026, signaling faster adoption in knowledge-based work.
- In 2027, overall displacement may reach 3.1%, as automation expands across services, logistics, and administrative functions.
- Generative AI alone is forecast to account for 0.8% of job losses in 2027, reflecting wider use of AI tools in content, analysis, and customer support.
- By 2028, AI-driven job displacement could reach 3.7%, with generative AI accounting for 28.4% of total losses.
- In 2029, the total impact is expected to reach 4.3%, indicating sustained structural shifts in workforce demand.
- Generative AI’s share may approach 29.6% by 2029, reinforcing its growing role in employment transitions.
- By 2030, AI and automation could affect 4.9% of U.S. jobs, with generative AI alone accounting for 1.5% and over 30.4% of total AI-related losses.
AI Job Loss Statistics By Countries
- According to techkv.com, in 2025, automation accounted for 2.6% of employment shifts in developed economies, compared with 0.9% in developing economies.
| Region/Country | 2025 AI impact |
| India | 270,000 white-collar jobs displaced (tech support, finance) |
| Sub-Saharan Africa | 17% employers warned of future risk |
| Latin America | Data-entry/transcription jobs down by 14% |
| Japan | Logistics/retail roles down by 3.2% |
| Germany & France | Reskilling support for more than 100,000 workers |
| Philippines | BPO full-time workforce down by 11.4% |
AI Job Loss Statistics By Sectors
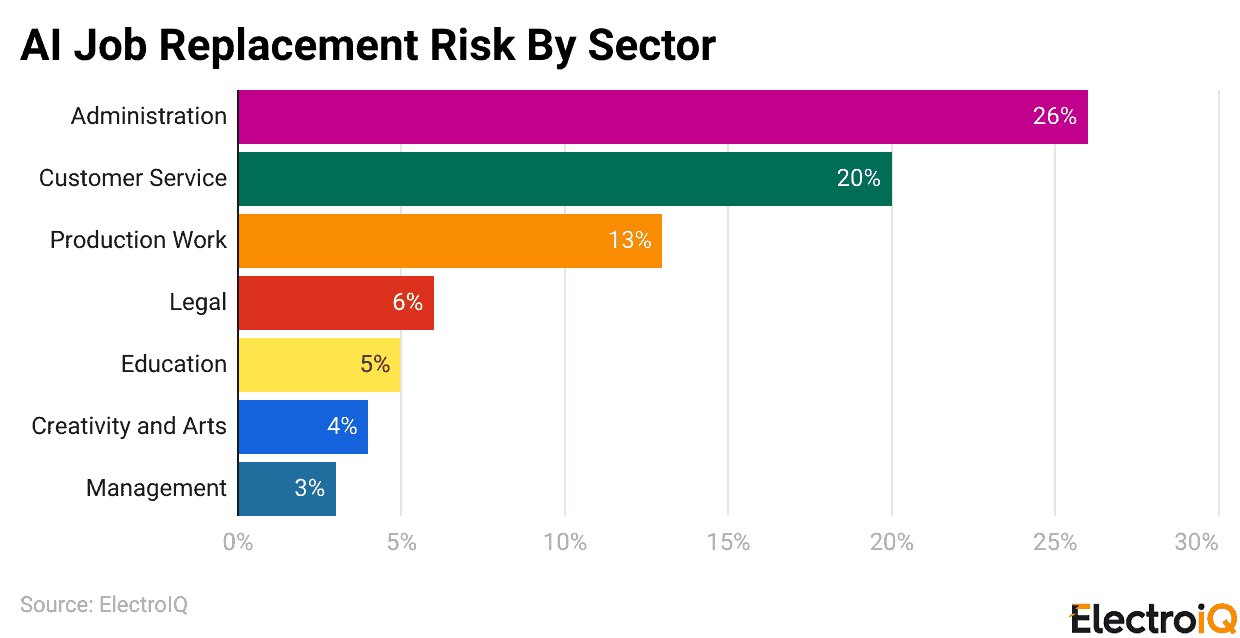
(Reference: techkv.com)
- In 2025, the most exposed sectors will be those with high levels of automatable tasks, with chatbots accounting for administration (26%) and customer service (20%).
- Production/manufacturing roles face a 13% risk as robotics grows, while legal work sits at 6% with AI aiding research and review.
- Meanwhile, Education has a 5% risk, creative jobs have a 4% risk, and management is the least affected at 3%.
By Job Roles
- According to Demand Sage, analyses indicate that AI may automate 80% of customer service representative tasks by 2025.
Moreover, the table below includes all the industries’ AI job risk analyses:
| Job role | Expected Automation Risk |
| Data entry and admin support | Up to 95% risk of automation. |
| Retail cashiers and checkout workers | About 65% by 2025. |
| Transportation and logistics roles | About 1.5M jobs will be lost by 2030. |
| Manufacturing workers | More than 50% by 2030. |
| Financial services roles | About 70% by 2025 and 54% high-risk. |
| Legal support staff | 80% paralegal work by 2026 and 65% researcher work by 2027. |
| Healthcare support roles | 99% medical transcription and 40% medical coding by 2025. |
| Content creation and media roles | 50% writers and 30% reporters by 2030. |
| HR support roles | 85% recruitment screening and 90% benefits admin between 2025 and 2027. |
- Data entry and administrative support roles remain the most vulnerable, with automation risk reaching up to 95% due to rule-based workflows.
- Retail cashier and checkout positions are projected to see around 65% of tasks automated as self-service and AI vision systems expand.
- Transportation and logistics sectors are expected to experience large-scale disruption, with nearly 1.5 million roles projected to decline by 2030.
- Manufacturing jobs face sustained pressure, as more than 50% of repetitive production tasks are expected to be automated by 2030.
- Financial services roles show elevated exposure, with about 70% of operational tasks at risk by 2025, particularly in back office functions.
- Legal support roles are undergoing structural change, with close to 80% of paralegal tasks and 65% of research activities projected for automation.
- Healthcare support functions such as medical transcription face near-complete automation, with risk levels approaching 99% by 2025.
- Content creation roles are being reshaped, as AI tools are expected to automate about 50% of basic writing tasks and 30% of reporting work by 2030.
- Human resources support roles show high exposure, with up to 90% of benefits administration and 85% of screening tasks automated between 2025 and 2027.
Estimated Job Loss Due To AI Implementation
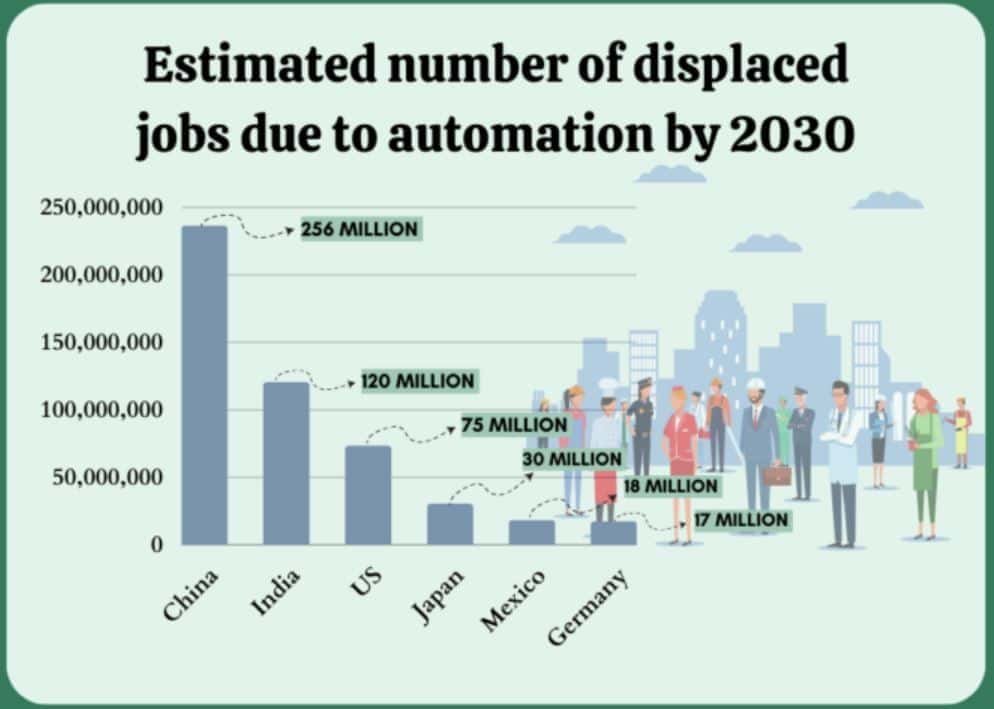
(Source: techjury.net)
- By 2030, job losses are expected to reach approximately 256 million in China.
- Other countries’ job losses are estimated at 120 million in India, followed by 75 million in the United States, 30 million in Japan, 18 million in Mexico, and 17 million in Germany.
Conclusion
After completing the article on AI Job Loss Statistics, it is now clear that employees across many sectors have lost their jobs due to AI implementations. Many reports suggested that routine, rule-based roles may shrink, but work will not vanish entirely. As AI increasingly reorganises organisations, it creates new roles.
This article estimates that analyses of the effects of adoption rates, government regulations, and business decisions vary across sectors and countries, but the overall effects will be uneven. Support and basic data jobs face a higher risk, while human-focused, creative, and oversight roles may grow.












