Introduction
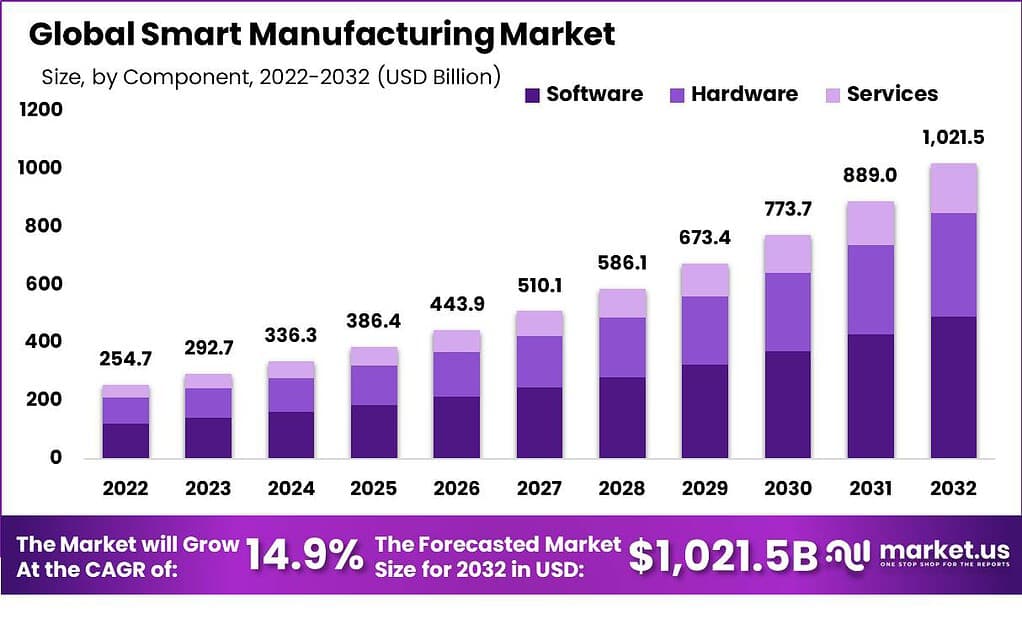
The Global Smart Manufacturing Market grows from USD 292.7 billion in 2023 to USD 1,021.5 billion by 2032 at a CAGR of 14.9% as factories use IoT, AI, analytics, and automation to improve efficiency and cut waste. The smart manufacturing market refers to the use of digital technologies to make industrial production more connected, automated, and data-driven.
It combines advanced hardware, software, and analytics to help factories monitor operations in real time, improve efficiency, and respond quickly to changes in demand or disruptions. Sensors, connected machines, and intelligent systems are used to turn traditional factories into responsive and adaptive production environments.
Smart manufacturing focuses on integrating physical production with digital intelligence. Machines, robots, and production lines are connected through industrial networks and cloud platforms, allowing data to flow across design, production, quality, and maintenance functions. This approach helps manufacturers reduce downtime, improve product consistency, and make better decisions based on actual shop-floor data rather than assumptions.
The market is closely linked to the broader shift toward Industry 4.0, where automation, connectivity, and intelligence are treated as long-term strategic capabilities. Manufacturers across automotive, electronics, food and beverages, chemicals, and heavy industry are adopting smart manufacturing to remain competitive, manage costs, and increase operational resilience in an uncertain global environment.
Top Key Takeaways
- Software leads components with 48.2% share, powering data analytics, IoT integration, and real-time optimization.
- Discrete control systems hold 21.8% share in technology, essential for assembly lines and automation in discrete manufacturing.
- Automotive end-use industry dominates with 23.6% share, driven by EV production, supply chain complexity, and precision needs.
- Asia Pacific commands 35.8% regional share, fueled by manufacturing hubs in China, Japan, and South Korea.
Key Statistics
- According to e-bi.com, 70% of manufacturers are expected to adopt IoT for real-time monitoring by 2025, improving visibility across production processes.
- The use of AI in manufacturing reduces defect rates by about 30%, mainly through advanced quality control and inspection systems.
- Predictive maintenance enabled by IoT helps cut equipment downtime by 50% and lowers maintenance costs by 40%.
- Around 60% of manufacturers use robotics for automation, leading to a 25% increase in productivity.
- Digital twins are projected to be adopted by 70% of manufacturers by 2030, helping reduce product development costs by 15%.
- Sustainable manufacturing practices can lower overall operational costs by 20%, supporting both efficiency and environmental goals.
- About 70% of manufacturers consider sustainability a key factor when making outsourcing decisions.
- In the medical device sector, 60% of manufacturers use 3D printing to produce custom implants and components.
- The use of AI in medical device manufacturing reduces scrap rates by around 30%, improving yield and material efficiency.
Top Driving Factors
Growth is being driven by the need to improve productivity while managing rising labor costs and skills shortages. Manufacturers are also under pressure to reduce waste, energy use, and production errors, which pushes adoption of real-time monitoring and automated quality control. In addition, the demand for faster product customization and shorter production cycles is encouraging factories to move away from rigid, manual processes toward flexible, software-controlled operations.
Demand Analysis
Demand is strongest among large and mid-sized manufacturers that operate complex production lines and face high costs from downtime or defects. These companies are investing in connected equipment, manufacturing execution systems, industrial IoT platforms, and advanced analytics to gain better visibility across operations.
Demand is also growing from smaller manufacturers that are adopting modular and scalable solutions, allowing them to start with basic monitoring and gradually expand toward more advanced automation and intelligence as their digital maturity increases.
Key Market Segment
By Component
- Hardware
- Software
- Services
By Technology
- Discrete Control Systems
- Human Machine Interface
- Machine Vision
- 3D Printing
- Machine Execution Systems
- Programmable Logic Controller
- Other Technologies
By End-Use Industry
- Automotive
- Aerospace & Defense
- Chemicals & Materials
- Healthcare
- Electronics
- Other End-Use Industries
Top Key Players
- ABB Ltd.
- Siemens AG
- General Electric
- Rockwell Automation Inc.
- Schneider Electric
- Honeywell International Inc.
- Emerson Electric Co.
- IBM Corporation
- Fujitsu Global
- Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
- 3D System, Inc.
- Fanuc U.K. Limited
- Cisco System, Inc
- Oracle Corporation
- Oracle
- Other Key Players
Use Cases
Predictive Maintenance
Smart manufacturing systems are widely used to monitor equipment health in real time. Sensors and connected machines continuously collect data on vibration, temperature, and operating conditions. This enables early detection of faults and helps prevent unplanned downtime. Maintenance activities are scheduled based on actual equipment condition rather than fixed intervals, improving asset life and operational reliability.
Production Process Optimization
Manufacturers use smart manufacturing platforms to analyze production line performance. Real-time data helps identify bottlenecks, idle time, and inefficiencies across machines and workflows. Process parameters are adjusted automatically to improve throughput and reduce waste. This use case supports consistent output quality and better utilization of resources.
Quality Inspection and Defect Detection
Advanced vision systems and analytics are applied to inspect products during and after production. These systems detect defects that are difficult to identify through manual inspection. Real-time feedback allows corrective actions to be taken immediately on the production line. This reduces rework, scrap rates, and customer returns.
Digital Twin Implementation
Digital twins are used to create virtual replicas of machines, production lines, or entire factories. These models simulate real-world operations using live data from the shop floor. Manufacturers use them to test process changes, new layouts, or equipment upgrades without disrupting operations. This lowers operational risk and supports better planning decisions.
Supply Chain and Inventory Management
Smart manufacturing solutions connect production data with inventory and supply chain systems. This provides visibility into raw material usage, work-in-progress, and finished goods levels. Demand fluctuations are addressed more quickly through data-driven production planning. As a result, inventory holding costs are reduced and order fulfillment becomes more reliable.
Energy Management and Sustainability
Energy consumption is tracked at machine and process levels using smart sensors and analytics. This helps identify energy-intensive operations and inefficiencies. Manufacturers use these insights to optimize energy usage and reduce operating costs. The use case also supports sustainability goals by lowering emissions and improving regulatory compliance.
Recent Development
- October, 2025 – ABB Ltd. refined its smart manufacturing strategy by strengthening automation software, digital control systems, and connected factory solutions to support flexible industrial operations.
- March, 2025 – Siemens AG expanded its smart manufacturing footprint by opening an advanced production facility focused on digital factory technologies and industrial artificial intelligence.
Conclusion
Smart manufacturing helps factories work better and save money by using smart technology to watch machines and make quick decisions. Software and automotive industries lead the growth, while Asia Pacific stays ahead due to big manufacturing countries. Even with high setup costs, companies will keep adopting these systems to stay competitive and meet growing demand for faster, better production.
Read More – https://market.us/report/smart-manufacturing-market/












