Introduction
Social Media and Eating Disorders Statistics: The connection between social media and mental health now exists as an undeniable fact because people spend their time viewing curated feeds that showcase perfect body images and attract billions of likes. Social media usage leads to eating disorders, which represent a serious mental health problem that includes content that results in disordered eating, body dissatisfaction, and obsessive behaviors about weight and shape.
Social media platforms function as cultural reflections and shape people’s body image and eating behavior, with global effects through 2025.
Editor’s Choice
- In 2025, 24% of daily social media–using high school students show symptoms consistent with eating disorders, indicating early vulnerability driven by online comparison.
- 18% of college students on image-based platforms like Instagram report a diagnosed eating disorder, reflecting the mental cost of curated perfection.
- Teens who spend more than three hours each day on social media platforms show a 72% higher probability of developing disordered eating patterns.
- 37% of teens report binge-eating episodes linked to late-night scrolling and emotional distress.
- 49% of female Instagram users link the Explore tab directly to body dissatisfaction.
- Eating disorders create a psychological load that affects depression 78.2% of the time and anxiety 74.5% of the time.
- 56% of users following weight-loss accounts admit to unhealthy dieting or fasting,g which social media trends have influenced.
- 67% of teens use filters to change their appearance before sharing posts, which creates a new body perception from the start.
- On TikTok, 43% of U.S. girls encounter eating disorder content, while 65% of them access mental health resources that provide helpful information.
- More than 5 million Americans who developed eating disorders identified their condition as starting after they spent too much time on social media.
- Disordered eating develops among 40% of LGBTQ+ youth who use social media to compare their appearance with others.
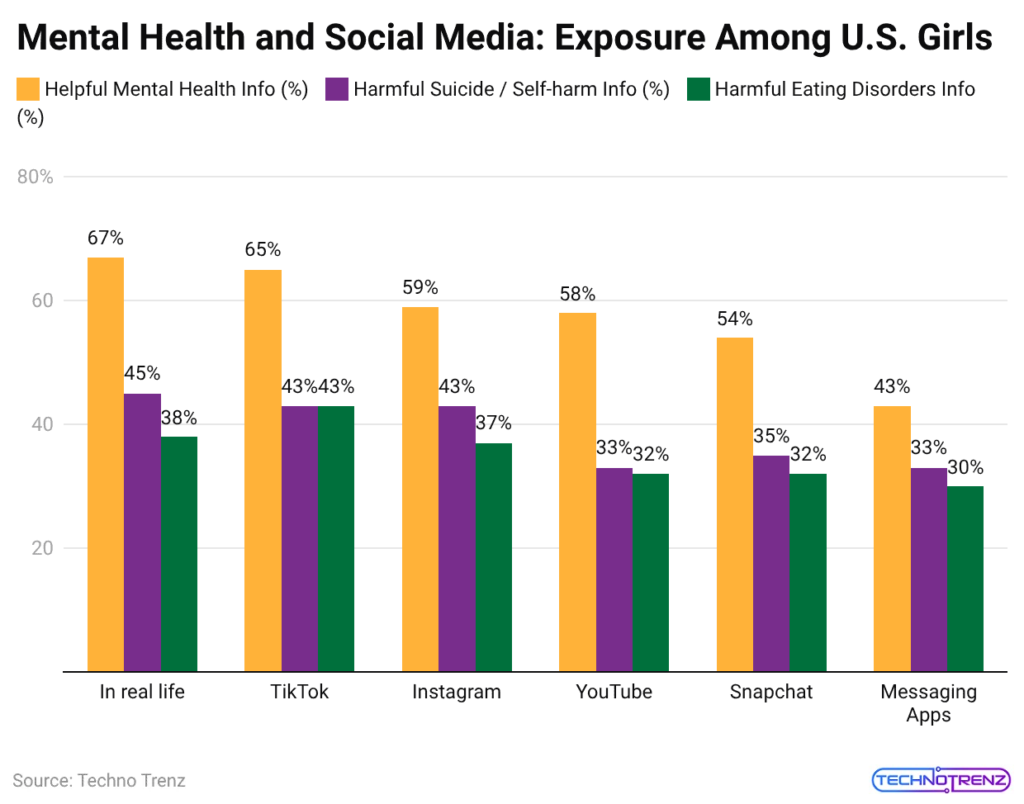
Mental Health Content Exposure For U.S. Girls Across Social Platforms
(Reference: sqmagazine.co.uk)
- The data from 2025 shows that young people use digital technology in a way that creates a contradiction between social media platforms, which help and harm their mental well-being.
- The online mental health information, which 67% of U.S. girls find useful through offline sources, presents a complicated situation according to their online experiences.
- On TikTok, 65% of users found helpful content,t but 43% of users encountered suicide or self-harm material, while 43% of users discovered eating disorder content,t which showed the system’s weak state between providing support and delivering harmful content.
- Users discovered positive resources through 59% of Snapchat users and 58% of Instagram users, yet approximately one-third to two-fifths of users experienced continuous contact with self-harm and disordered eating content.
- Users of Snapchat and other messaging applications observe the same pattern: they see harmful content while seeing fewer positive materials.
- The data shows policymakers and platform operators that they must change their algorithms because social media platforms for preventing eating disorders should have more power than they currently give to harmful content.
How Social Platforms Are Shaping Body Image Perceptions
- The 2025 data shows an alarming link between social media platforms and eating disorders, which keeps growing stronger.
- The current social media usage rate among high school students, who use it daily, shows that 24% of them show eating disorder symptoms, which proves that constant social comparison creates early eating disorder risk.
- The psychological effects of visible perfection on Instagram and other image-based platforms lead 18% of college students to develop a diagnosed condition related to body image.
- 56 % of users who watch weight-loss content experience dietary disorders through their fasting and dieting practices.
- The second statement shows that 35 % of adults between 18 and 25 years old skip meals or purge their food to achieve a more attractive online appearance.
- The social media content that Americans watch today leads to 5 million people developing disorders in 2025.
- The risk increases for LGBTQ+ youth because 40% of them develop disordered eating patterns when they compare themselves to others.
- Social media platforms, together with eating disorders,s create a public health crisis which exists because users experience visual pressure and algorithms direct their content consumption.
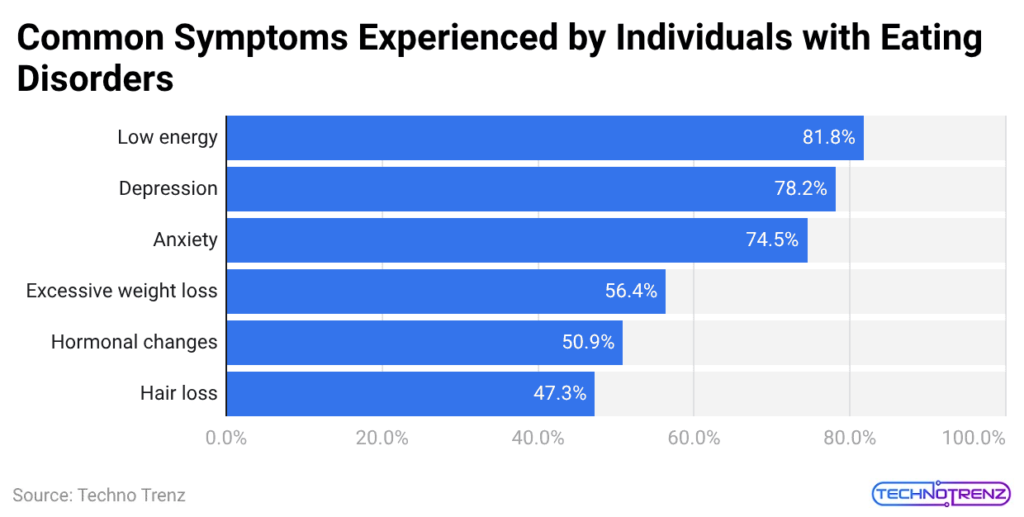
Key Physical And Psychological Warning Signs of Eating Disorders
(Reference: sqmagazine.co.uk)
- The above data by SQ Magazine shows that social media use and eating disorders lead to two types of health problems, which show mental and physical deterioration.
- The 2025 data shows that 81.8 % of people suffered from low energy because they lacked proper nutrition,n whereas 78.2 % of people dealt with depression, and 74.5 % of people experienced anxiety.
- The mental health effects become worse in places where people measure their success through comparison to others.
- More than half of the participants experienced weight loss beyond normal limits, while 50.9% developed hormonal disturbance,s which indicates internal body stress.
- Social media platforms drive eating disorder development, as shown by hair loss (47.3%), which demonstrates how the condition affects both mental health and physical body.
- The increasing overlap between social media use and eating disorder behavior creates a situation that requires both early identification methods and social media platforms to take their corporate responsibility.
How Screen Time Intensity Shapes Disordered Eating Patterns
- The 2025 data demonstrates how extended screen usage impacts human behavior by increasing their risk of developing eating disorders.
- Teens who use platforms for more than three hours a day face a 72 % increased risk of developing disordered eating patterns, whereas users who spend 4 to 6 hours daily face a 2.4 times greater chance of developing restrictive dieting tendencies compared to users who spend less time.
- The main factor that triggers late-night scrolling is negative emotion, which causes 37 % of people to binge eat.
- The comparison culture creates behavioral changes in 48 % of high-screen-time teenagers who associate their body dissatisfaction with changes in their eating patterns.
- Users who check their apps more than 10 times a day are 3 times more likely to develop food guilt, which affects 31% of college students who eat less to achieve current “fasted” aesthetics.
- Social media platforms and TikTok content that promotes food-related content increasingly connect with eating disorders among young people.
- Social media platforms and eating disorders operate as a feedback loop in which users’ visibility and trend visibility create social validation, which leads to the development of unhealthy habits.
- Social media platforms and eating disorders need current solutions that require both content exposure restrictions and design improvements for content development.
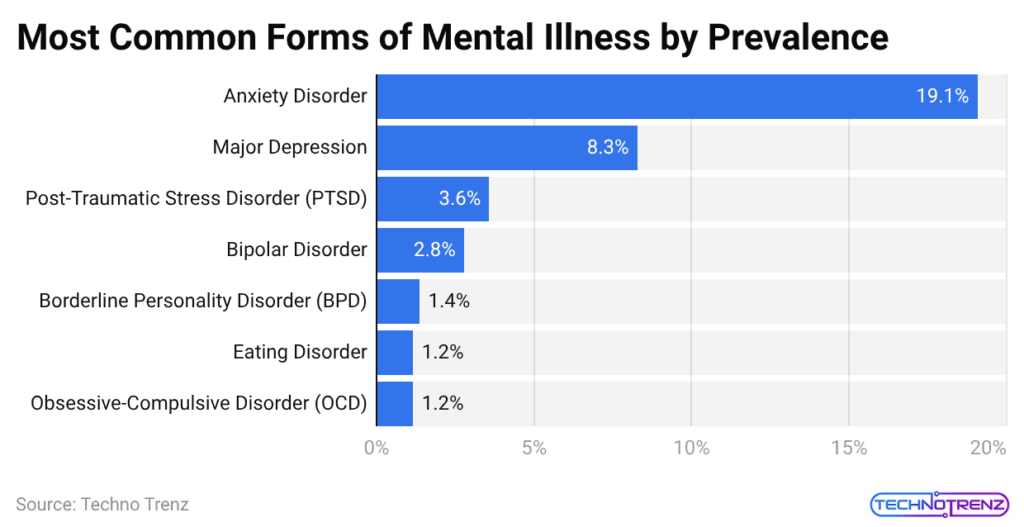
A Snapshot of The Most Prevalent Mental Health Conditions
(Reference: sqmagazine.co.uk)
- The data indicate that mental health issues show a specific pattern of distribution. People with anxiety disorders represent the highest %age of the population who experience anxiety, which affects 19.1 of every 100 people.
- Major depression follows at 8.3%, which impacts 1 in 12 people who also experience anxiety symptoms.
- The worldwide population experiences millions of mid-tier conditions, which include PTSD (3.6%) and bipolar disorder (2.8%), that cause severe functional disabilities yet have lower rates of occurrence.
- Although eating disorders and OCD both report 1.2% prevalence, they present extremely dangerous health threats because of their high mortality rates.
- The increasing impact of social media, together with eating disorders, indicates that actual rates of eating disorders are lower than they should be becausethe first symptoms go unnoticed.
- The relationship between social media, eating disorders, anxiety, and depression creates a cycle that increases mental health problems because online stress makes people more prone to mental health issues.
Major Social Platforms Are Shaping Eating Disorder Trends
- Platform-specific dynamics function as the main element that fast-tracks eating disorder (ED) growth for 2025.
- TikTok stands out as the most influential trigger environment, with 74% of users under 21 encountering weight-related content weekly and over 9 billion views tied to #bodygoals alone—signalling massive algorithmic amplification.
- Alarmingly, 42% of teens aged 13–17 report exposure to ED-promoting content within their first month, highlighting early-risk immersion.
- Instagram’s Explore tab continues to intensify comparison culture, with 49% of female users linking it to body dissatisfaction and 34% being algorithmically nudged toward pro-diet content without intent.
- The new platforms Threads and Lemon8 show a 22% increase in eating restriction practices, which demonstrate that these dangers show no signs of decreasing.
- People with eating disorders show increasing social media use because platform design, content discovery, and visual design create their patterns of behavior.
- The connection between social media and eating disorders has reached a point where social media platforms must take responsibility for their content.
Psychological Impact of Beauty Filters And Digital Alteration Tools
- The 2025 data shows that filters are no longer playful enhancements—they are psychological conditioning tools.
- Digital modification has become a major force in self-identity development, which begins at 11.8 years when 67% of teens start to change their appearance for social media posts.
- Nearly half of young females feel their real appearance isn’t “post-worthy,” while 36% of users report heightened social anxiety linked to editing tools.
- People experience reality detachment, which results in 42% of people feeling disconnected from their mirror image, and 21% of study participants report increased body dissatisfaction after 10 minutes of filter exposure, according to controlled studies.
- Face-tuning apps serve as relapse triggers for 58% of people in recovery because they create harmful trends of self-monitoring behavior.
- Social media platforms now show their users beauty filters, which 81% of under-18 TikTok users use to create content that promotes eating disorders through algorithmic design.
- The solution to social media and eating disorder problems requires a complete redesign of digital beauty development and consumption processes.
Research Breakthroughs and Policy Shifts Addressing Digital Eating Disorder Risks
- The 2025 date represents a critical milestone because it changes how analysts view institutional responses to social media and eating disorder connections.
- New research from the American Psychological Association shows that youth heavily exposed to aesthetic-driven content are 1.7 times more likely to develop eating disorder symptoms, while engagement-based algorithms increase harmful body-image exposure by 68%.
- The findings match a CDC–NIH report, which observed a 9% annual increase in ED hospitalizations for teen girls who mentioned social media as a treatment trigger.
- TikTok and Instagram now allow third-party moderation audits, while AI-based hashtag detection has decreased dangerous content exposure for underage users by 33%. Meta treated 34 million posts as policy violations because they contained health misinformation.
- 70% of parents support restrictions on algorithmic profiling while bipartisan legislators advocate for a Digital Mental Health Bill of Rights.
- The developments show that social media platforms need better technology to fight eating disorders,s which requires ongoing public health education initiatives.
Conclusion
Social Media and Eating Disorders Statistics: The 2025 evidence creates an unchangeable truth because social media platforms and eating disorders now exist as interconnected systems that operate through their design, their algorithms, and their visual culture. The platforms that claim to provide inspiration and connection actually increase social comparison and perfectionistic tendencies and dangerous behaviors, which spread throughout their user base. The recent policy developments, together with AI content moderation solutions,s represent positive progress, but organizations need to establish preventive measures that go beyond mere content removal.
The process of creating effective organizational change requires organizations to develop new ways of engaging people, which should include restrictions on appearance-based content distribution and programs that teach digital literacy from the beginning. The relationship between social media and eating disorders has advanced to the point where organizations need to implement preventive measures that protect psychological safety as an equal priority with organizational growth, user visibility, and commercial gain.
FAQ
Social media increases disordered eating patterns by its ability to spread content that focuses on appearance, its function of making users compare themselves to others, and its system, which gives priority to weight loss content and ideal body standards.
Recent research found that approximately 24 % of high school students who use social media daily developed symptoms that match eating disorder criteria.
TikTok shows the highest exposure because 43 % of girls who use the platform see eating disorder material, while 74 % of users under 21 encounter weight-related content every week.
Over 5 million Americans in 2025 reported that prolonged social media exposure contributed directly to the onset of their eating disorder.
Approximately 40% of LGBTQ+ youth report disordered eating patterns driven by appearance-based comparison and online validation pressure.












