Introduction
GDPR Statistics: The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) serves as the most effective protection of personal privacy rights because it governs privacy rights through standardized enforcement methods. The GDPR, which became law in May 2018, established new rules for organizations to follow when handling personal data, but businesses must now change their data management practices or face penalties that exceed multiple million-dollar amounts.
The GDPR enforcement system reached its developed stage by 2025, when breach incidents increased, and fines remained high, together with regulatory activities that became more organized. The GDPR functions as a legal instrument that adapts to changing technology because it now addresses AI systems, international data transfers, and widespread digital monitoring.
This article presents complete research-based GDPR statistics that show current trends about GDPR violations, which cost businesses money through fines and breach notifications, which serve as security alerts.
Editor’s Choice
- The European Union imposed its largest GDPR fine, which amounts to €1.2 billion against Meta, demonstrating a new level of enforcement power.
- Amazon faced €746 million in fines, which became its second-largest penalty, leading to increased examination of major technology companies.
- The Media Telecoms and Broadcasting industry has received the highest total fines, which amount to €3,994.71 million, which exceeds the total fines of Industry and Commerce by nearly four times.
- The highest fines result from violations that breach general data processing principles because they total €2,431.93 million.
- The absence of legal permission for processing activities has resulted in total fines of €1,966.51 million.
- The absence of proper security controls between technical and organizational areas resulted in penalties amounting to €836.52 million.
- The commercial aspect of business operations creates privacy conflicts, which result in 46.9% of compliance requirements for organizations.
- Organizations that have established advanced privacy systems face 38% lower costs for handling security breaches.
- The absence of a Cybersecurity Incident Response Plan (CSIRP), which 77% of organizations do not possess, creates a major security risk that increases their chances of facing enforcement actions.
GDPR Largest Fines Issued For Violations
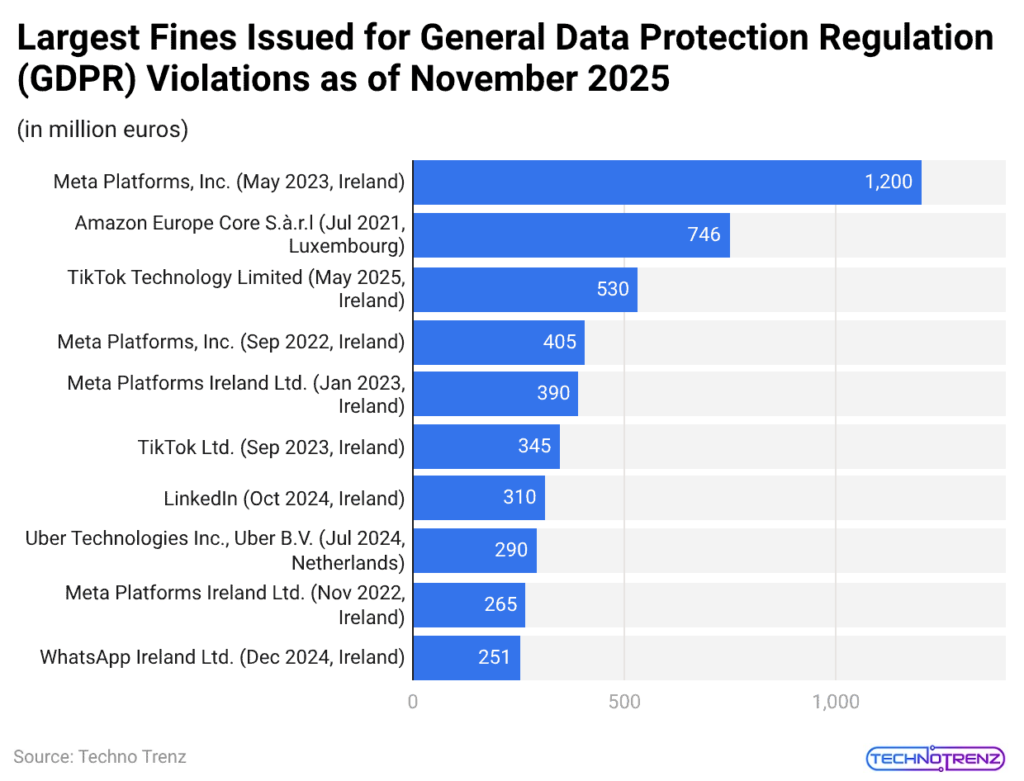
(Reference: statista.com)
- The chart demonstrates both the total number of European Union members who face severe privacy violations and their respective violation numbers.
- The highest fine which has ever been imposed under GDPR belongs to Meta Platforms (Ireland, May 2023), which received a penalty of €1.2 billion.
- Amazon follows at €746 million, while TikTok’s May 2025 penalty reached €530 million, reinforcing regulators’ scrutiny of cross-border data transfers.
- The corporate environment of Meta shows multiple compliance breakdowns through additional fines of €405 million, €390 million, and €265 million.
- LinkedIn, Uber, and WhatsApp received major fines, which included penalties of €310 million, €290 million, and €251 million, respectively.
- The above GDPR statistics reveal two critical trends: enforcement disproportionately targets data-intensive tech giants, and penalties are escalating into multi-hundred-million-euro territory.
- The data shows that the most important EU enforcement actions result from major governance breakdowns instead of insignificant procedural mistakes.
Highest GDPR Fines For Regulations By Industry
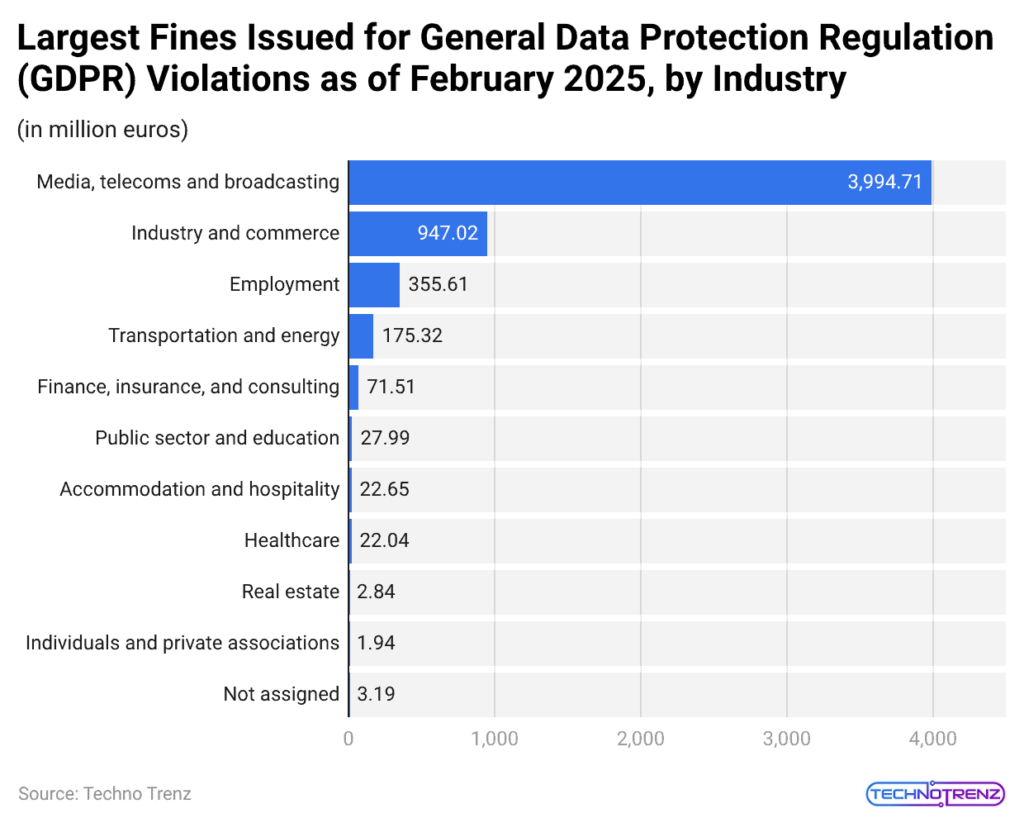
(Reference: statista.com)
- The chart shows a major discrepancy in GDPR statistics because Media and Telecoms and Broadcasting together received penalties of €3,994.71 million, which equals four times the total penalties of Industry and Commerce, which reached €947.02 million.
- Employment-related violations follow at €355.61 million, while Transportation and Energy stand at €175.32 million.
- The financial services industry reported €71.51 million in expenses, which resulted from stricter compliance requirements.
- The combined Healthcare and Hospitality sectors maintained their spending below €25 million for each sector.
- GDPR statistics show how data-intensive industries receive enforcement actions because digital advertising and content platforms and international data transfers create the largest regulatory challenges, which will emerge in 2025.
Highest GDPR Fines Issued By Type Of Violation
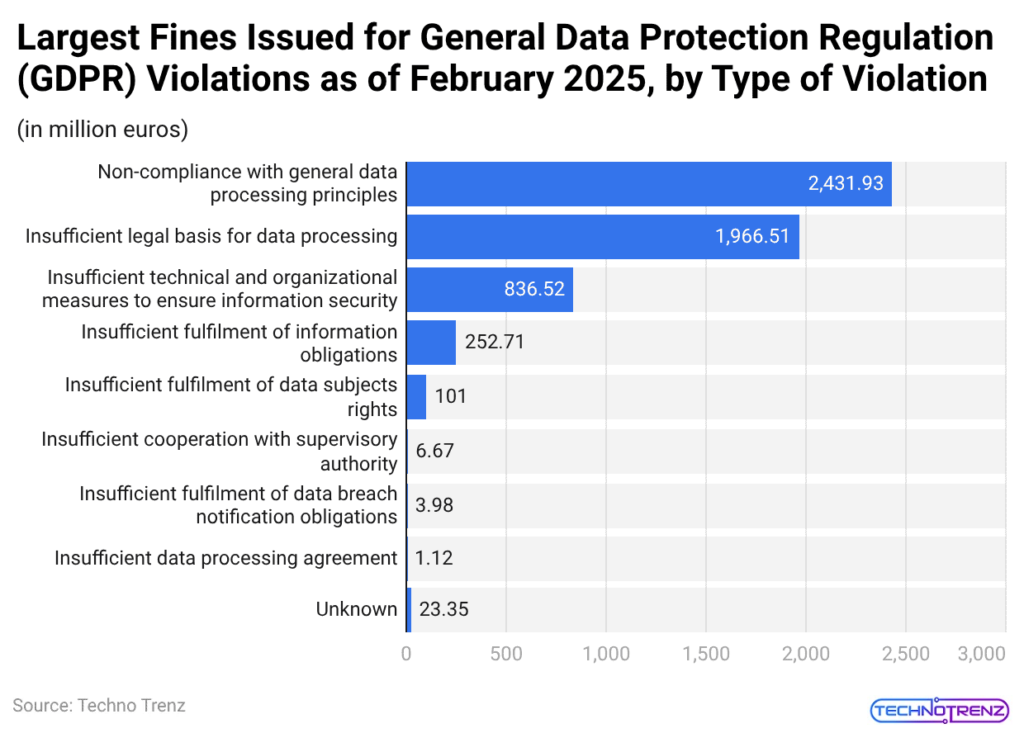
(Reference: statista.com)
- The chart provides an effective visual overview of GDPR data, showing how regulators allocate their enforcement resources.
- The largest fines stem from non-compliance with general data processing principles, totaling €2,431.93 million, which shows how transparency and fairness, together with accountability failures, lead to the most severe sanctions.
- The insufficient legal basis for data processing, which costs €1,966.51 million, shows how organizations still face difficulties with obtaining consent and conducting lawful processing activities.
- The security deficiencies result in high costs, as organizations face fines totaling €836.52 million for their lack of proper technical and organizational controls.
- The organization shows persistent governance deficiencies through its information obligation failures, which cost €252.71 million, and data subject rights violations, which cost €101 million.
- The GDPR statistics show that regulators focus their enforcement efforts on structural compliance failures while they overlook operational violations.
- The enforcement system relies on principle-based violations because it operates according to fundamental governance standards, while it focuses on handling foundational compliance problems, which need organizations to develop proactive compliance systems.
Commercial Priorities Vs. GDPR Compliance
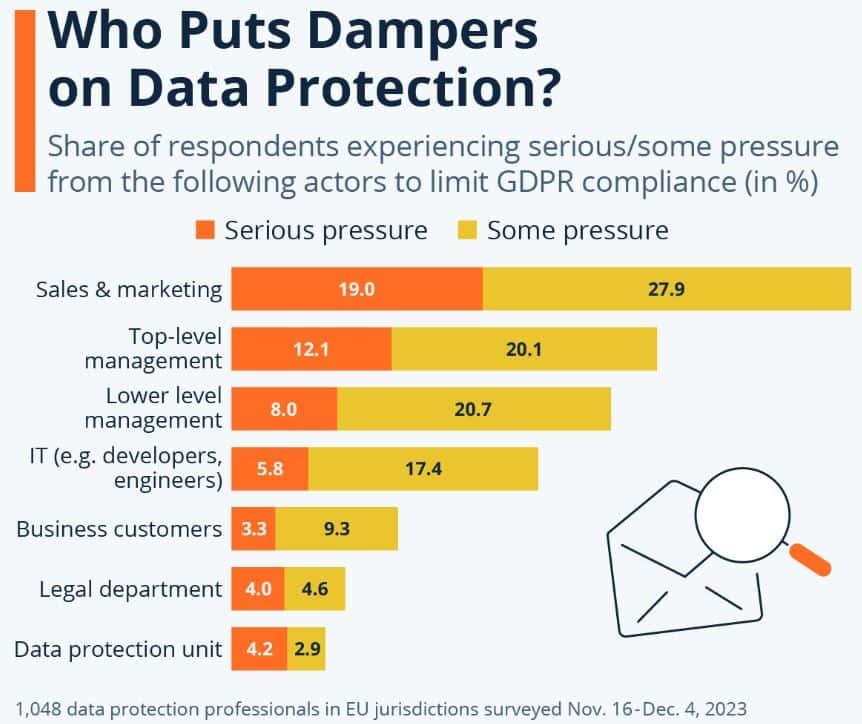
(Source: statista.com)
- The European Center for Digital Rights’ latest survey results show how businesses actually handle their data protection tasks.
- The chart shows that organizations face two opposing needs that create a commercial compliance conflict.
- Sales and marketing create the most pressure because 19.0% of people experience intense pressure, while 27.9% of people deal with moderate pressure.
- The total 46.9% marks the highest rate among all operational groups. Top-level management follows at 32.2% combined pressure, while lower-level management reaches 28.7% of total pressure.
- The operational friction that exists in data-driven systems results in IT teams delivering 23.2% of their work.
- The legal departments (8.6% total) and data protection units (7.1% total) operate with less than half of their normal work pressure.
- The statistics about GDPR compliance show that businesses resist compliance because they need to generate revenue.
- Internal governance culture stands as the primary enforcement obstacle, according to the GDPR statistics, which show that regulatory absence does not create enforcement problems.
- The GDPR, which began enforcement in May 2018, aims to stop global technology companies, including Alphabet, Amazon, and Meta, from using their data for exploitation.
- The Digital Markets Act (DMA) and Digital Services Act (DSA) create additional regulatory frameworks that expand Europe’s existing regulatory framework.
- The billion-euro fines imposed on Meta demonstrate the enforcement power of regulatory authorities.
- Organizations demonstrate inconsistent compliance throughout their daily activities according to survey results.
- The Dutch data protection officer used the term “fighting a tidal wave” to explain the difficulties of implementing GDPR because he found compliance efforts were extremely difficult.
- After five years of training programs, knowledge gaps still exist because business needs take precedence over privacy recommendations.
GDPR’s Impact On Email Marketing
- The developing GDPR statistics demonstrate how consent requirements changed the email marketing methods used by businesses.
- More than 57% of companies from Europe, North America, and Oceania chose to deliver “Privacy Policy Changed” alerts instead of sending re-consent requests because they preferred less demanding ways to meet regulations.
- The performance metrics improved because email open rates had a 19% increase, while click-through rates reached a 14% rise since 2014.
- The research results show that more stringent consent requirements, which include double opt-in systems, have improved audience quality.
- The GDPR statistics show that databases that organizations build through approved permissions create less regulatory risk while delivering better engagement results and sustainable digital marketing outcomes.
Global Consumer Data Privacy Trends And Risk Exposure
- The year 2024 will bring about a major transformation in how consumers understand data about their personal information.
- The implementation of privacy laws by 13 U.S. states has created new regulations that reflect growing public concern about data handling practices.
- Consumers now pay closer attention to how businesses handle their personal data collection, storage, and monetization processes.
- A significant security threat exists because 77% of organizations do not have a Cybersecurity Incident Response Plan (CSIRP), which puts both their operations and customer safety at risk.
- The trends that exist now connect to the overall GDPR statistics, which show that organizations must meet higher compliance standards while authorities increase their enforcement efforts.
- The global system of data governance, which protects consumer rights, has now moved toward greater accountability through GDPR and state-level reforms.
Financial Consequences And Competitive Advantages Of GDPR Enforcement
- The financial effects and strategic benefits of GDPR enforcement create 15 different financial impacts throughout businesses.
- The enforcement of GDPR creates financial penalties that have the power to change business operations and market positioning of companies.
- The current regulations permit fines that can reach either €20 million or 4% of a company’s total yearly income, which creates substantial balance sheet liabilities for international businesses.
- The GDPR statistics show that organizations that experience privacy violations now face financial risks that extend beyond regular compliance expenses.
- Data breaches and regulatory scrutiny create a situation that damages customer trust while reducing customer participation and making it harder for businesses to achieve their long-term conversion goals.
- Organizations that spend resources on advanced privacy systems experience actual business benefits since research shows that regulated companies achieve 38% lower costs from data breaches than their unregulated competitors.
- Organizations use privacy management processes to defend their data as a way to build their business strategy.
- Businesses achieve better brand trustworthiness and higher customer loyalty through strong compliance, which enables them to use their regulatory compliance as a strategic edge in the market.
GDPR Regulatory Evolution And Emerging Compliance Frontiers
- The current phase of GDPR enforcement has become more complex because it now requires advanced technological capabilities.
- The ongoing dispute over cross-border data transfers reached a critical point when TikTok received a €530 million fine, which revealed fundamental conflicts between EU data sovereignty requirements and global data transfer standards.
- The cases that regulators use to demonstrate their enforcement capabilities through GDPR statistics show how they impose severe fines when security measures do not work.
- Major platforms such as Google and Shein face cookie consent violations, which demonstrate their ongoing difficulties with providing complete transparency.
- Authorities now investigate automated decision-making systems, AI-based profiling systems, and biometric technologies, which include facial recognition.
- The emergence of new technical risks has replaced previous compliance issues as the main factor driving changes in GDPR statistical data.
- The core principles of lawfulness, fairness, transparency, and purpose limitation face testing through accelerating innovation, which transforms how businesses implement privacy practices in an AI-powered world.
Conclusion
GDPR Statistics: The GDPR began as a compliance requirement but has developed into a fundamental framework that affects worldwide data economic systems. The enforcement operations now focus on fundamental organizational shortcomings, which become evident through the combination of billion-euro fines, media and telecom sector consolidation, and basic rule violations that drive organizational violations.
The 2025 GDPR enforcement, which extends to automatic decision-making and international data transmission, has evolved into a digital marketplace advantage that goes beyond its function as a legal framework.
FAQ
The largest GDPR fine is €1.2 billion, imposed on Meta in May 2023.
Media, Telecoms, and Broadcasting lead with €3,994.71 million in total penalties.
Non-compliance with general data processing principles, totaling €2,431.93 million.
Up to €20 million or 4% of global annual revenue, whichever is higher.
TikTok received a €530 million fine linked to cross-border data transfer violations.
Amazon, with a €746 million penalty.
13 states enacted laws, with 9 currently active laws.












