Circular Economy Trade Finance is a specialized form of financial support that helps businesses trade goods and materials in ways that align with circular economy principles – meaning products are reused, recycled, or remanufactured instead of being discarded after a single use. This approach encourages companies to design supply chains that minimize waste, extend product lifecycles, and prioritize resource efficiency, all while maintaining the flow of commerce across borders.
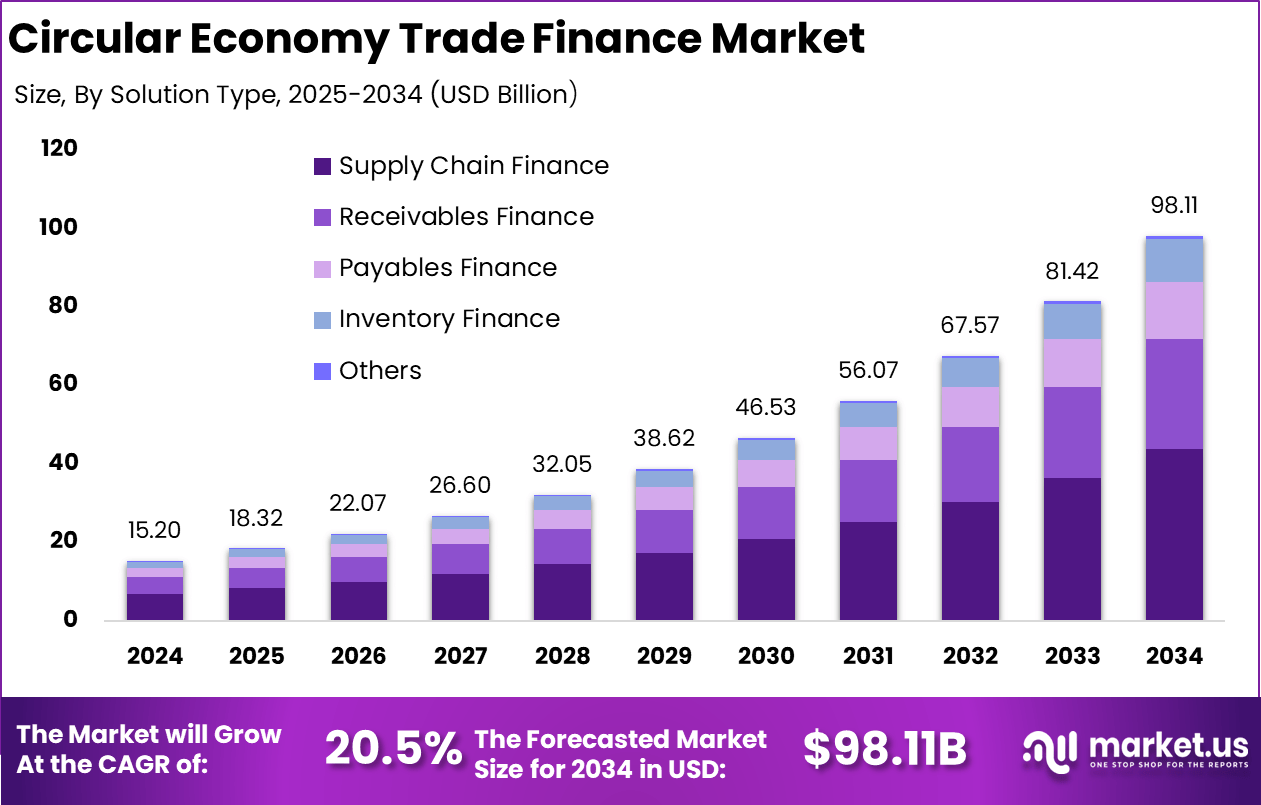
According to Market.us, The global circular economy trade finance market is projected to reach USD 98.11 billion by 2034, rising from USD 15.20 billion in 2024 and advancing at a 20.5 percent CAGR from 2025 to 2034. North America held a leading position in 2024 with a market share of more than 38.6%, representing about USD 5.86 billion in revenue.
Generative AI is playing a growing role in Circular Economy Trade Finance by helping companies design smarter, more efficient circular supply chains and financial products. AI tools can analyze vast amounts of data to identify opportunities for reuse, optimize recycling routes, and predict demand for refurbished goods, making it easier for businesses to shift from linear to circular models. For example, AI-powered platforms can now automate the creation of sustainability-linked loan agreements, track the lifecycle of traded materials, and even simulate the environmental impact of different circular strategies before they are implemented.
One of the most notable trends is the integration of AI with blockchain and IoT technologies to enhance transparency and traceability in circular supply chains. Over 60% of recent circular trade finance deals now use blockchain for real-time tracking, and AI is increasingly used to automate compliance checks and sustainability reporting. Another trend is the rise of sustainability-linked lending and green bonds, which now account for about 40% of new financing deals in the sector, with AI helping to verify and measure the environmental outcomes of these investments.
AI-driven analytics and blockchain are now central to ensuring transparency and compliance in circular trade finance. Over 60% of recent deals use blockchain for real-time tracking of materials, enabling financiers and regulators to verify the origin, use, and recycling status of traded goods. AI-powered compliance systems automate risk assessments, flag suspicious transactions, and streamline reporting, helping businesses meet strict regulatory requirements and avoid costly penalties. This digital layer also reduces fraud and strengthens trust among stakeholders, making it easier for companies to access financing for circular projects.
In practice, major banks and financial institutions are deploying these technologies to support circular economy initiatives. For example, in 2025, several global banks launched dedicated circular finance programs, using AI to assess the environmental impact of projects and blockchain to track material flows. These deployments are not limited to large corporations; startups and SMEs are also benefiting from tailored financial products that support circular business models, such as leasing, product-as-a-service, and remanufacturing.
Market Dynamics
Driver: Rising Global Sustainability Commitments
Growing global commitments to sustainability and climate goals are driving the circular economy trade finance market. Governments, businesses, and financial institutions are increasingly prioritizing circular business models that focus on resource efficiency, waste reduction, and recycling. This shift is supported by regulatory frameworks and international agreements, such as the Paris Agreement and Sustainable Development Goals, which encourage investment in eco-friendly projects and supply chains.
The expansion of green bonds and sustainability-linked loans is also fueling growth in this sector. Financial institutions are developing tailored products that fund circular initiatives, such as redesigning production lines and using recycled inputs. As more companies seek to meet ESG standards, demand for circular trade finance solutions is rising, creating new opportunities for banks and investors.
Restraint: Complexity in Standardization and Impact Measurement
A major restraint in the circular economy trade finance market is the lack of standardized frameworks for measuring impact and assessing risk. Circular economy projects span diverse industries and processes, making it difficult for financiers to evaluate their environmental and financial viability. Small and medium enterprises (SMEs) often struggle to demonstrate sustainability credentials due to limited resources and expertise, which restricts their access to financing.
Regulatory compliance is also complex, as definitions and standards for circular economy activities vary across regions. This inconsistency creates hurdles for cross-border financing and scaling circular initiatives. Without clear international standards, financial institutions remain cautious about providing large-scale funding, limiting the broader adoption of circular trade finance products.
Opportunity: Digital Transformation and Cross-Border Collaboration
Digital transformation is opening new opportunities in circular economy trade finance. Technologies like blockchain and IoT are being used to track resources and verify the impact of circular projects, increasing transparency and accountability. Over 60% of recent circular trade finance deals now incorporate blockchain for real-time tracking, which helps build trust among stakeholders and streamlines funding processes.
Cross-border collaborations and public-private partnerships are also gaining momentum. These partnerships help overcome funding gaps and improve capital flows toward recycling, waste management, and resource recovery projects, especially in emerging markets. As digital platforms and collaborative models mature, the circular economy trade finance market is poised for rapid expansion.
Challenge: Limited Awareness and Expertise
Limited awareness and expertise in circular economy concepts remain a significant challenge for market growth. Many businesses, investors, and financiers lack the knowledge to identify, quantify, and finance circular projects effectively. This knowledge gap prevents the scaling of circular trade finance solutions beyond early adopters and slows overall market development.
Financial institutions often require specialized training and resources to assess circular projects, which can be costly and time-consuming. As a result, circular finance products are still largely concentrated among large enterprises with established ESG practices. Expanding awareness and building expertise across the sector will be essential for unlocking the full potential of circular economy trade finance.
Looking ahead, the future of circular trade finance will be shaped by deeper integration of AI, blockchain, and IoT, enabling real-time monitoring, predictive analytics, and automated compliance. Public-private partnerships are expected to grow, especially in emerging markets, to fund infrastructure and close financing gaps for circular projects. As these technologies mature, circular trade finance will become more accessible, transparent, and resilient, supporting a global shift toward sustainable economic models.












