Smart City Market Size
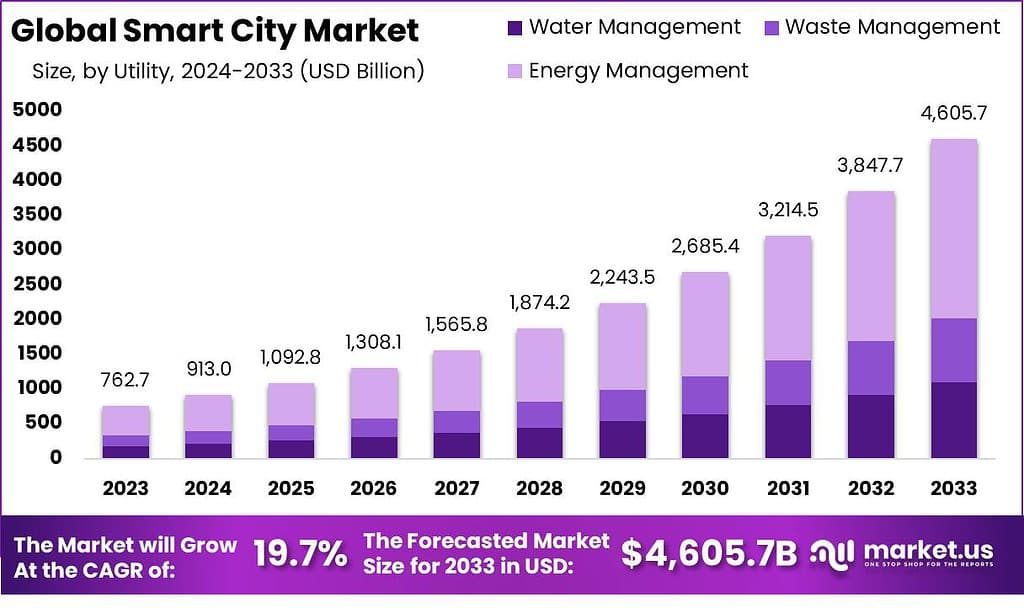
According to Market.us, The global smart city industry is undergoing significant growth, moving from a base of USD 762.7 billion in 2023 to an expected value of around USD 4,605.7 billion by 2033. This expansion reflects a robust compound annual growth rate of 19.7% between 2024 and 2033.
The upward trajectory is being driven by rising urbanization, large-scale investment in digital infrastructure, and the growing need for sustainable city management. Key areas such as transportation, utilities, and public safety are increasingly supported by connected technologies, enabling cities to deliver more efficient and responsive services to their populations.
Smart City Statistics
- The market is projected to grow from USD 762.7 billion in 2023 to around USD 4,605.7 billion by 2033, registering a strong CAGR of 19.7%.
- Smart utilities led the applications with a 30% share, reflecting high adoption in energy, water, and waste management systems.
- Smart infrastructure accounted for more than 28% of the market, underlining the importance of connected buildings and advanced city frameworks.
- Within utilities, energy management was the leading segment with a commanding 56% share, showing rising focus on sustainable power usage.
- In transportation, the intelligent transportation system (ITS) segment held a 47% share, highlighting the push for traffic efficiency and smart mobility.
- North America remained the largest regional market with 32% share, supported by strong investments in digital infrastructure and urban modernization.
Market Overview
The Smart City market focuses on developing urban areas that integrate technology, data analytics, and interconnected systems to improve the quality of life, enhance resource management, and optimize city operations. These cities use technologies such as IoT (Internet of Things), artificial intelligence (AI), big data, and 5G to create efficient public services like smart transportation, intelligent energy grids, security, waste management, and citizen engagement platforms.
The market covers diverse sectors, including smart utilities, smart governance, smart buildings, and healthcare services, aiming to create sustainable, resilient cities. Top driving factors fueling the Smart City market include rapid urbanization – with more than 60% of the global population expected to live in urban areas by 2030 – alongside the urgent need to manage resources and reduce environmental impacts.
Growing concerns about traffic congestion, energy consumption, and public safety also push governments and private sectors to invest heavily. Technologies like AI-driven traffic management systems have been shown to reduce travel time and fuel consumption, highlighting the demand for smart solutions that enhance operational efficiency.
Analysts’ Viewpoint
Demand analysis reveals strong growth in Asia-Pacific and North America, with North America holding over 32% of the market share, supported by substantial government incentives and technological adoption. Sustainable infrastructure and energy management are critical areas, with the energy segment commanding nearly 56% of the utility market. The public sector’s increasing adoption of smart governance, which includes video surveillance and enhanced security measures, is expected to grow fastest, driven by the need for better accountability and citizen engagement.
The surge in adoption of enabling technologies meticulously shapes the market. IoT remains the backbone, with 30.7 billion connected devices worldwide by 2025 projected to reach over 75 billion, fueling data-driven city operations. Cloud computing, AI, machine learning, and big data analytics complement IoT to analyze vast data streams for actionable insights. 5G deployment enhances connectivity and real-time processing, critical for smart transportation and emergency response systems.
Role of Generative AI
The role of generative AI in the smart city market is becoming increasingly important, powering over 30% of smart city applications by 2025. This includes urban mobility, public safety, utility management, and infrastructure optimization. Cities worldwide are leveraging generative AI technologies to analyze vast amounts of real-time data, enabling smarter decision-making that improves operational efficiency and quality of life. Surveys indicate that over 60% of cities have integrated AI technologies into at least one aspect of urban life, reflecting widespread adoption and growing investment in AI-driven smart city projects.
Generative AI supports intelligent urban planning by simulating and predicting urban dynamics, helping city planners optimize resource distribution and reduce environmental impact. This capability accelerates the development of scalable, sustainable, and citizen-friendly urban environments. The increasing adoption of AI-powered systems is driving demand for advanced smart city technologies such as AI-enabled IoT sensors, autonomous traffic systems, and AI-based crime detection.
Emerging trends
Emerging trends in the smart city market highlight significant advancements in AI-powered transit, IoT waste management systems, smart building technologies, and 5G/6G connectivity. AI-driven intelligent transportation systems that manage traffic flow and reduce congestion are among the fastest-growing segments.
A surge in smart utility infrastructure, including energy-efficient grids and water management, is also notable, supported by data analytics platforms that optimize usage and detect faults proactively. The adoption of 5G networks is increasing data transmission speeds, enabling real-time monitoring and control across city-wide smart systems.
Urban agriculture and green infrastructure, supported by smart monitoring and AI automation, are emerging trends aimed at promoting sustainability. These mechanisms improve air quality, optimize water usage, and enhance food production within city limits, thereby contributing to environmental resilience. In parallel, smart citizen services such as e-governance and AI-supported healthcare continue to gain traction, fueled by demand for more responsive and personalized urban services. These trends collectively drive a shift toward fully integrated, data-driven urban ecosystems that aim to improve the overall quality of urban life.
Growth factors
Growth factors propelling the smart city market include rapid urbanization, technological innovation, and increasing government funding for smart infrastructure. Over half of the global population now lives in urban areas, creating pressing needs for sustainable, efficient city services to manage resources like energy, water, transportation, and public safety. Accelerating adoption of IoT devices and AI-enabled platforms facilitates real-time data collection and actionable insights, leading to smarter resource management and cost savings. The market experiences yearly growth rates exceeding 15%, bolstered by heavy investments in smart transportation, smart utilities, and intelligent building management systems.
Environmental concerns and regulatory pressures to reduce carbon footprints further drive innovation and adoption in smart city solutions. Cities aim to reduce energy consumption and waste production while enhancing resilience against natural disasters through predictive analytics and AI-enabled monitoring. Private sector partnerships and collaborations between governments and technology providers supply necessary capital and expertise, pushing forward projects that improve urban sustainability and livability.
Driver Analysis
Growing Urban Challenges Demand Smarter Infrastructure
One key driver pushing smart city development is the increasing pressure on urban infrastructure caused by rapid population growth, traffic congestion, and environmental pollution. Cities face challenges like overcrowded roads, limited access to public transit, and poor air quality. For instance, rising traffic jams and pollution spur cities to rethink and upgrade their transportation systems and public utilities. These urgent needs drive investments in intelligent infrastructure that prioritizes efficiency, sustainability, and improved quality of life through technology integration.
The adoption of advanced technologies like artificial intelligence, IoT sensors, and data analytics allows city planners to address these mounting urban pressures with smarter solutions. These technologies enable monitoring and predictive management of traffic flows, energy usage, and public safety. For example, AI-powered traffic control systems can optimize signals to reduce congestion, while IoT devices track environmental factors like air quality and waste levels.
Restraint Analysis
High Implementation Costs and Resource Limitations
One significant restraint hindering the widespread adoption of smart cities is the high cost of implementing the required technology infrastructure. Developing smart grids, installing sensors across utilities, traffic systems, and integrating AI-driven tools demand substantial financial resources that many cities struggle to allocate. For instance, smaller or financially constrained municipalities may find it difficult to fund the extensive technology upgrades while managing other essential urban services. These budgetary limitations can slow down the rollout of smart city projects or result in fragmented and uneven development.
Besides the financial hurdle, there is also a lack of uniformity in standards and interoperability between different technologies, which complicates integration and increases costs further. Additionally, cities need continuous investment in upgrading and maintaining technology systems, which requires long-term funding commitments. These monetary and resource challenges create barriers, making some urban areas unable to fully adopt or sustain smart city infrastructure despite the potential benefits.
Opportunity Analysis
Enhanced Citizen Engagement and Public Services
The development of smart cities creates new opportunities for improving citizen engagement and the delivery of public services. Digital platforms enable residents to interact directly with city authorities, report issues, and access services conveniently. For example, mobile apps and online portals allow citizens to pay taxes, request maintenance, or participate in local government decisions efficiently. This increased transparency and participation can foster trust and lead to more responsive and tailored urban governance.
Furthermore, smart city technologies open avenues to enhance public safety, healthcare, and education through real-time data monitoring and predictive analytics. Cities can deploy sensors and AI to monitor emergencies, pollution levels, or infrastructure health, allowing quicker, data-driven responses. These improvements not only boost residents’ quality of life but also create business opportunities for startups and technology providers focused on innovating urban solutions. The growing emphasis on sustainable and human-centered design further supports long-term urban well-being and smarter community development.
Challenge Analysis
Data Privacy and Trust Concerns
A major challenge for smart city projects is managing residents’ data privacy and building public trust. The extensive collection and analysis of data from sensors, cameras, and personal devices raise concerns about surveillance and misuse of personal information. For instance, citizens may worry that their movements, behaviors, or communications are being tracked without adequate protections or transparency. This skepticism can lead to resistance against smart city initiatives despite their advantages.
City planners must therefore implement strict data governance frameworks that ensure legal, ethical, and secure handling of information. Transparent communication about data usage and strong safeguards are essential to gain and maintain trust. Without this, smart city projects risk falling short of public acceptance, undermining their effectiveness. Governments and technology providers must demonstrate a commitment to protecting privacy while balancing safety and operational needs to overcome this critical barrier.
Key Market Segments
Based on Application
- Smart Governance
- Smart Building
- Environmental Solution
- Smart Utilities
- Smart Transportation
- Smart Healthcare
- Other Application
Based on Governance
- City Surveillance
- C.S.
- E-governance
- Smart Lighting
- Smart Infrastructure
Based on Utility
- Water Management
- Waste Management
- Energy Management
Based on Smart Transportation
- Intelligent Transportation System
- Parking Management
- Smart Ticketing & Travel Assistance
Read More – https://market.us/report/smart-city-market/












